Figure 3. Theoretical Model of the Interaction Between WML and Markers of Neuroinflammation and Angiogenesis Based on Current Results and Review of the Literature.
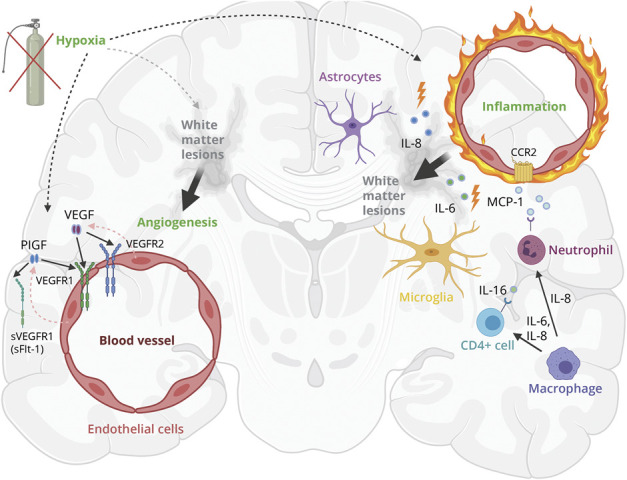
Hypoxia induces neuroinflammation and endothelial cells, microglia, and astrocytes release proinflammatory markers IL-8 and IL-6 and IL-16 and MCP-1. Those cytokines could be involved in WML pathology by BBB disruption and disruption of the neurovascular unit, resulting in gliosis and thus WML.19 Hypoxia and neuroinflammation could stimulate upregulation of PlGF and VEGF, inducing pathologic angiogenesis in damaged white matter in the acute phase.11,19,48 This original figure was designed for this article and created with BioRender.com. IL = interleukin; MCP-1 = monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; PlGF = placental growth factor; sVEGFR1 = soluble VEGF receptor 1 (same as sFlt-1); VEGF = vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A and VEFG-D); VEGFR1/VEGFR2 = VEGF receptor 1/2; WML = white matter lesions.
