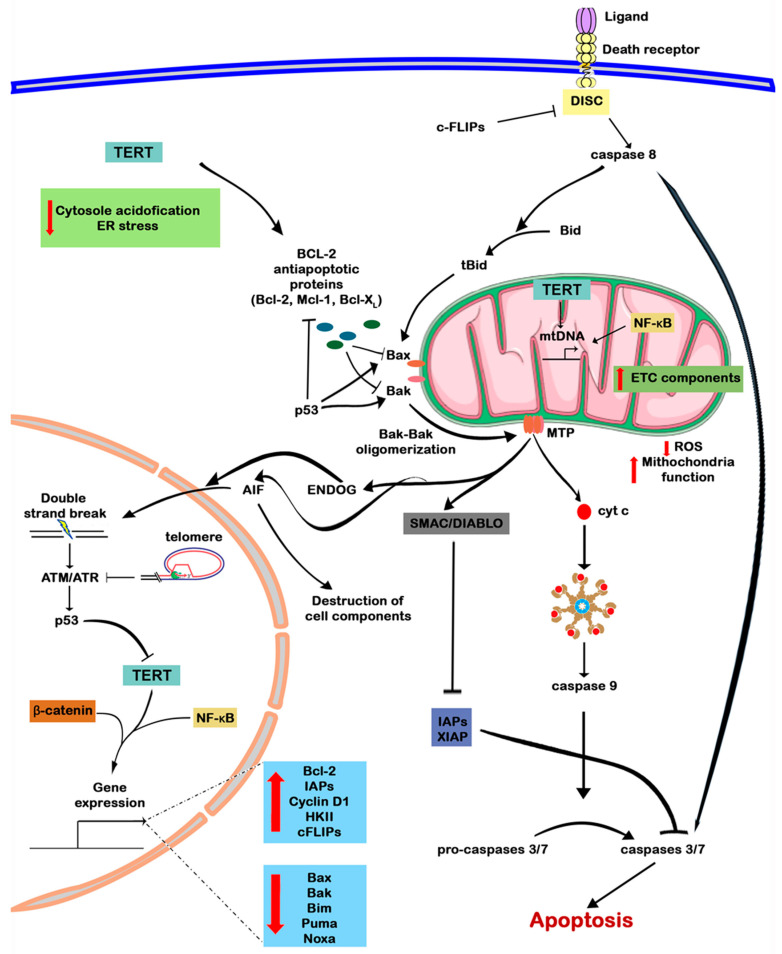
Figure 4.
In the nucleus, TERT performs both canonical (elongates telomeric ends) and non-canonical functions (participates in the regulation of gene expression). Maintenance of a normal telomere structure suppresses ATM/ATR signaling and thus reduces the activity of p53, a negative telomerase regulator. TERT alone or together with transcription factors of NF-κB, Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways stimulates the expression of anti-apoptotic factors, reducing the level of pro-apoptotic. In the cytoplasm, it diminishes cytosol acidification and prevents the ER stress-response progression. TERT contains a BH3-like domain which can probably bind to proteins of the BCL-2 family and regulate apoptosis. In mitochondria, telomerase reduces the level of ROS production and restores mitochondrial function. Additionally, TERT is likely to be involved in mitochondrial DNA repair and regulation of mitochondrial gene expression. Hence, BCL-2 family proteins are regulated at the transcriptional level and by protein–protein interactions with telomerase and p53. Oligomerization of proapoptotic proteins Bax and Bak leads to the formation of MOMP and the release of cyt c, SMAC/DIABLO, AIF and ENDOG from mitochondria. Cyt c in the cytoplasm induces apoptosome assembly by interacting with Apaf1 and pro-caspase 9, which leads to the activation of caspase 9 and further triggering of the cascade of caspases through activation of caspases 3 and 7 and, finally, to cell death by apoptosis. Normally, caspases are blocked by IAPs and XIAP, but SMAC/DIABLO released from mitochondria blocks them. AIF and ENDOG induce destruction of intracellular contents, along with DNA cleavage, followed by activation of ATM/ATR signaling. Apoptosis can also be induced by an external pathway from the death receptor and the formation of the DISC complex, which can be inhibited by c-FLIPs. The DISC assembly activates caspase 8, which can either directly trigger a cascade of caspases, or proteolytically cleave Bid to form tBid, which triggers the oligomerization of Bax–Bak. The up arrow (red) means increase and the down arrow (red) means decrease.