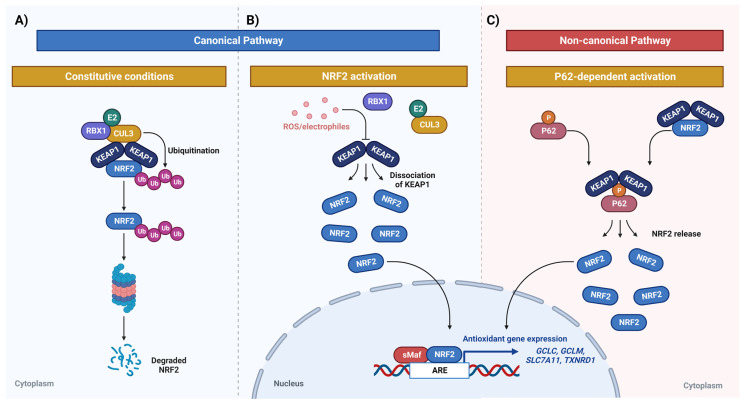
Figure 1.
Canonical and non-canonical NRF2 pathways. (A) NRF2 proteasomal degradation under constitutive conditions. The ETGE and DLG motifs of NRF2 bind to the KEAP1 Kelch domains; this binding causes the ubiquitin ligase CUL3/RBX1 E2 to join the complex, in which CUL3 acts as a scaffold protein that binds to the BTB domain of KEAP1, allowing the formation of a complex with a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2). (B) Under oxidative and/or electrophilic stress, KEAP1 undergoes a conformational change, which interrupts the Kelch/DLG binding and leads to its detachment from NRF2, thus the degradation of NRF2 is interrupted and it translocates to the nucleus. (C) Non-canonical pathway of P62-mediated NRF2 activation. When autophagic flux is compromised and P62 accumulates, KEAP1 is sequestered by P62 and does not bind to NRF2, stopping its degradation. Created with BioRender.