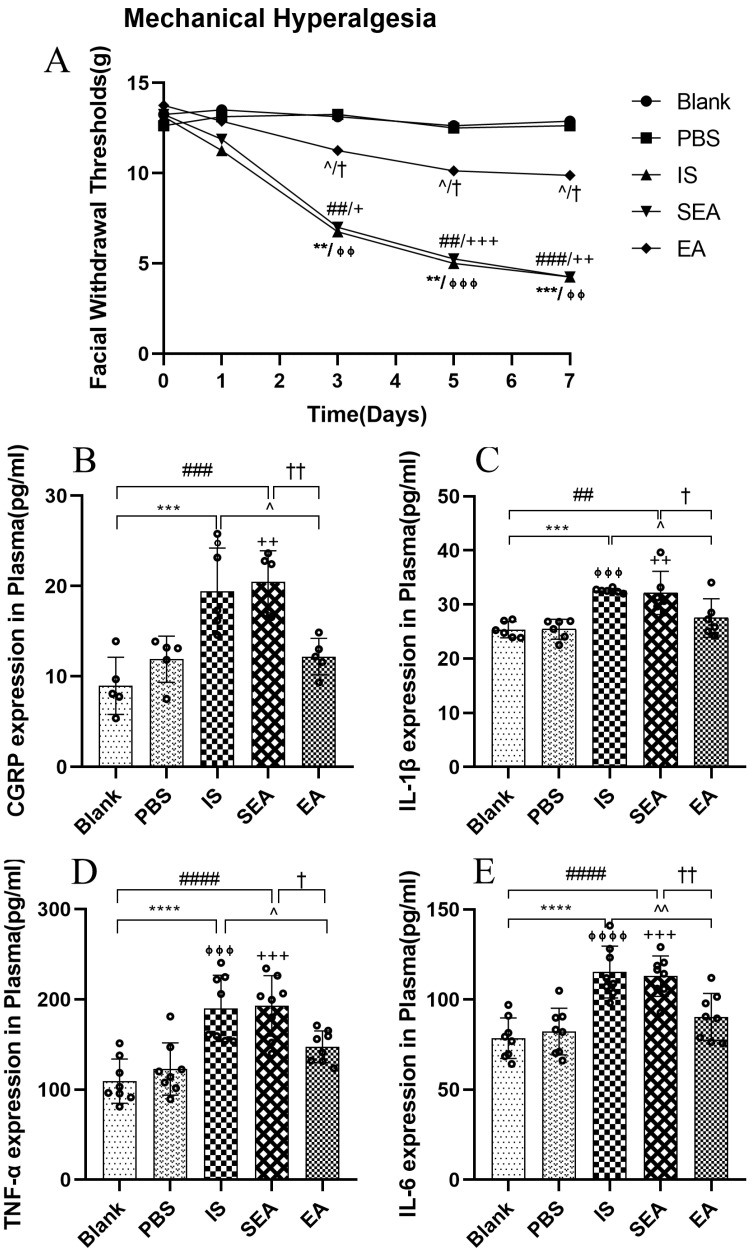
Figure 2.
(A) The changes in facial mechanical withdrawal thresholds in the five groups of rats (n = 8/group). Repeated daily IS-dural administrations induced basal mechanical response decreases and EA treatment at GB20/34 alleviated the facial mechanical withdrawal thresholds in rats following dural IS stimulation. Plasma levels of CGRP (B) and inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β (C), TNF-α (D), and IL-6 (E), in the five groups of rats detected by ELISA (n = 6–8/group). Repeated IS infusions into dura increased the release of CGRP and the above inflammatory cytokines, while EA decreased plasma levels of CGRP and inflammatory cytokines. Kruskal–Wallis test was used to analyse facial mechanical withdrawal thresholds followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons. ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis test were used to analyse ELISA data. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001, Blank vs. IS; ⏀ p < 0.05, ⏀⏀ p < 0.01, ⏀⏀⏀ p < 0.001, ⏀⏀⏀⏀ p < 0.0001, PBS vs. IS; ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001, #### p < 0.0001, Blank vs. SEA; + p < 0.05, ++ p < 0.01, +++ p < 0.001, PBS vs. SEA; ^ p < 0.05, ^^ p < 0.01, IS vs. EA; † p < 0.05, †† p < 0.01, SEA vs. EA.