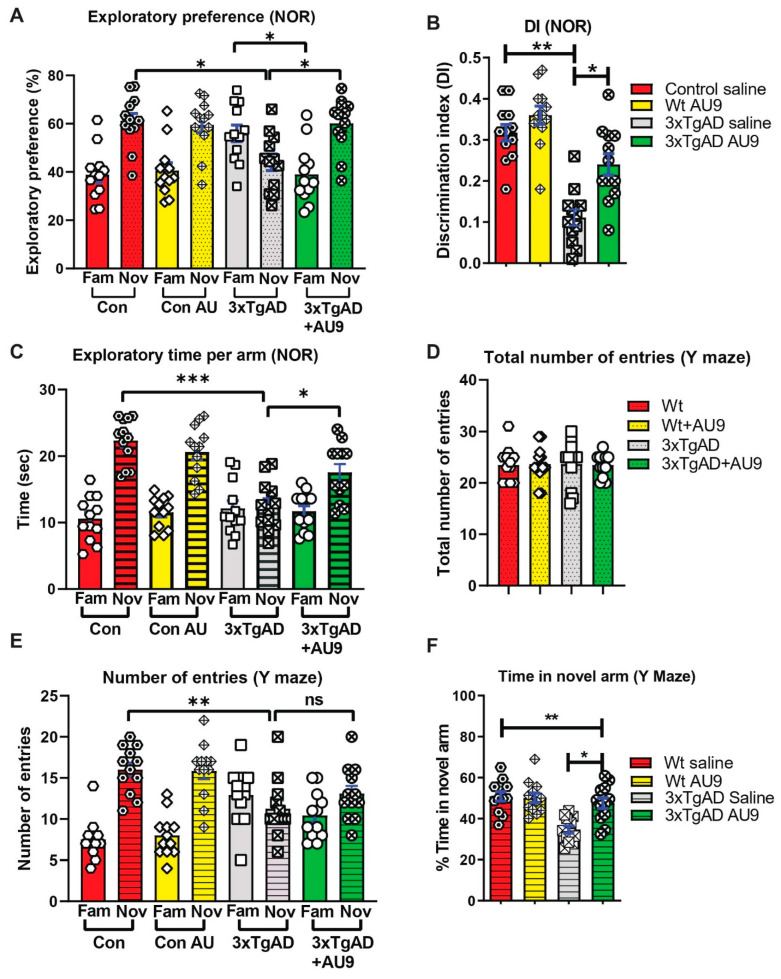
Figure 4.
AU9 improves memory deficits in 3xTgAD mice. (A) Results for novel object recognition (NOR) tests reflect an exploratory preference for the novel object vs. the familiar object by the animals that were analyzed by a naive subject. (B) Discrimination index (DI), represents the recognition of memory sensitivity. Where discrimination index was calculated as (DI) (T novel − T familiar)/(T familiar + T novel). (C) The exploratory time of a novel object when compared to the familiar object. (D) Results from Y-maze tests for the total number of entries into the novel and familiar arms. (E) Results from Y-maze tests for the number of times in the novel or familiar (other) arm. (F) The Y-maze tests for the percent time the animal spends in the novel arm. Statistical values were obtained by student t test analysis ± S.E.M. Where n = 12 mice per group and ns represents no significance, where * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.001 and *** p < 0.0001.