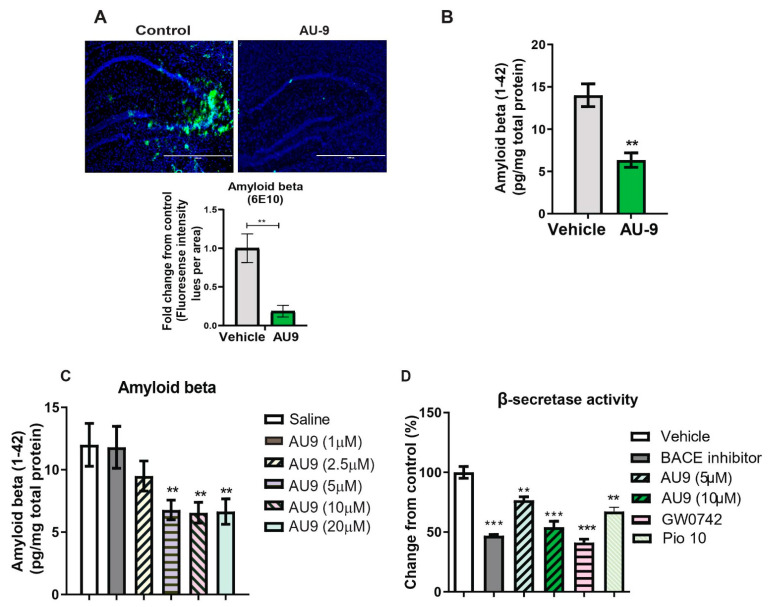
Figure 7.
AU9 reduces amyloid beta (1-42) levels in 3xTgAD mice. (A) Immunofluorescence imaging (anti-6E10 antibody) shows a reduction in levels of all forms of Amyloid beta levels in 12-month-old 3xTgAD mice treated with AU9 orally for three months (5 mg/Kg daily). Densitometric measurements of Amyloid beta in hippocampi from six mice and four slices per mouse. Values were standardized to total area. (B) Elisa measurement of soluble form of Amyloid beta (1–42) from mice treated in the same manner as mice as in panel A. Amyloid beta was measured from hippocampi from six mice per group. Values were based on a standard curve of Amyloid beta 1–42 and standardized to total protein concentrations. Statistical values were obtained using Student t-test analysis ± S.E.M. Where n = 6 mice per group and ** p < 0.001. (C) Reduction of Amyloid-beta being secreted in media from APP-Cho cells following increasing concentrations of AU9 treatment (1, 2.5, 5, 10 and 20 µM). Values were based upon standardized curve from ELISA (R&D Systems). Statistical values were obtained using student t-test analysis ± S.E.M. Where n = 6 independent experiments were repeated in triplicate per group and **: p < 0.001. (D) Effects of AU9 (5 µM and 10 µM) on Beta secretase activity in APP-Cho cells. β-Secretase activity was determined fluorometrically using an β-Secretase activity kit (Biovision, Waltham, MA) and standardized to total protein concentration from APP-Cho cells. Beta-secretase activity was represented as relative fluorescence unit per mg of total protein. Values were based upon means from 6 independent repetitions with 3 replicates in each group and represented as a percent change from control. Statistical values were obtained using student t-test analysis ± S.E.M. **: p<0.001, ***: p < 0.0001.