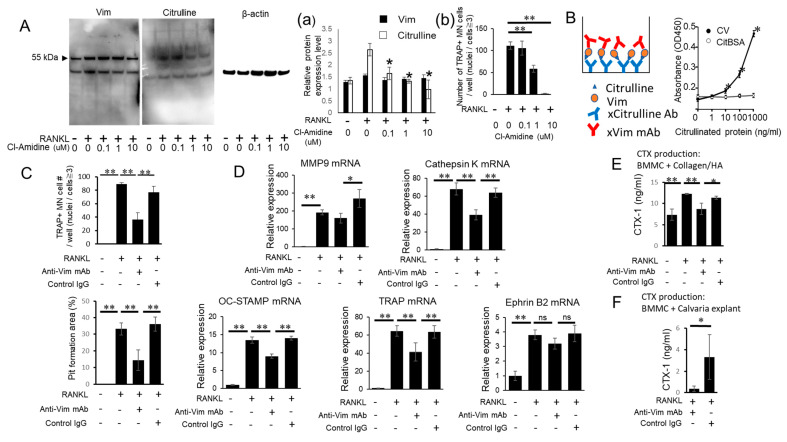
Figure 2.
Possible engagement of Cl-amidine-sensitive PAD in the citrullination of vimentin and anti-vimentin mAb-mediated interruption of CV-induced OC-genesis. (A) OC precursors were stimulated with or without RANKL (50 ng/mL) and/or Cl-amidine. After 24 h, supernatant and cell lysates were collected and vimentin (Vim) or citrulline was detected by Western blotting using the antibodies described in the Materials and Methods section. Protein bands were measured by densitometry to determine the levels of Vim, citrulline and β-actin and relative expression of Vim and citrulline was calculated in comparison with an internal control of β-actin (Figure 2(Aa)). After 6 days of above-noted OC-genesis conditions, TRAP staining was performed (Figure 2(Ab)). (B) Sandwich ELISA to determine citrullination of Vim. Anti-citrulline antibody was used as a capture antibody and anti-Vim antibody as a detection antibody. Different concentrations of CV and citrullinated BSA (CitBSA) (0, 1, 10, 100 and 1000 ng/mL) were used as a sample. (C,D) OC precursors were stimulated with RANKL in the presence or absence of anti-Vim mAb or control IgG for 48 h or 7 days with the addition of fresh medium every 3 days. TRAP staining, pit formation assays and qPCR were performed. (E,F) OC precursors were cultured on a type I collagen-treated hydroxyapatite coating plate (E) or on murine calvaria bone disks (F). After 7 days, the supernatant was applied to CTX-1 ELISA. All in vitro assays were performed in triplicate and the results were expressed as the mean ± SD. All experiments were independently repeated three times. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01. #: number.