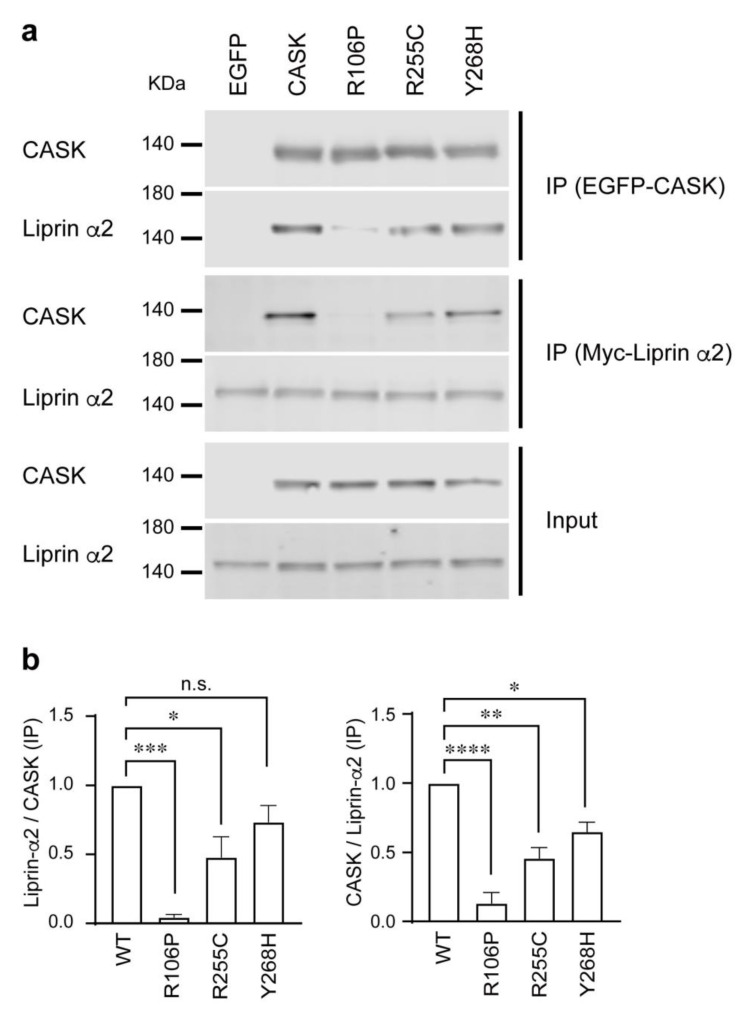
Figure 8.
Deleterious mutations affect CASK-Liprin-α2 interaction. (a) Western blotting images for immunoprecipitation for analyzing binding affinity between CASK mutants and Liprin-α2. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with EGFP alone, EGFP fused wild-type or mutant CASK harboring either R106P, E255C, or Y268H mutations and Myc-tagged Liprin-α2 constructs. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP (IP EGFP-CASK) or anti-Myc antibody conjugated beads (IP Myc-Liprin). Input and immunoprecipitated proteins were subjected to Western blotting using anti-CASK or anti-Myc antibodies for measurement of binding affinity. (b) Binding affinity between Liprin-α2 and CASK missense mutants was measured by the co-precipitation efficiency. (Left) Summary graph for affinity measurement by immunoprecipitation with anti-EGFP antibody conjugated beads blotted with anti-Liprin antibody. The signal intensity was normalized by the one co-transfected with wild-type CASK. (Right) Summary graph for affinity measurement by immunoprecipitation with anti-Myc antibody conjugated beads blotted with anti-CASK antibody. The signal intensity was normalized by the one co-transfected with wild-type CASK. Coimmunoprecipitation experiments were repeated three times. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA, n.s. = not significant.