Figure 1. Structural and functional comparison of Ace-DEX cGAMP MPs formulated via monoaxial or coaxial electrospray to activate BMDCs in vitro.
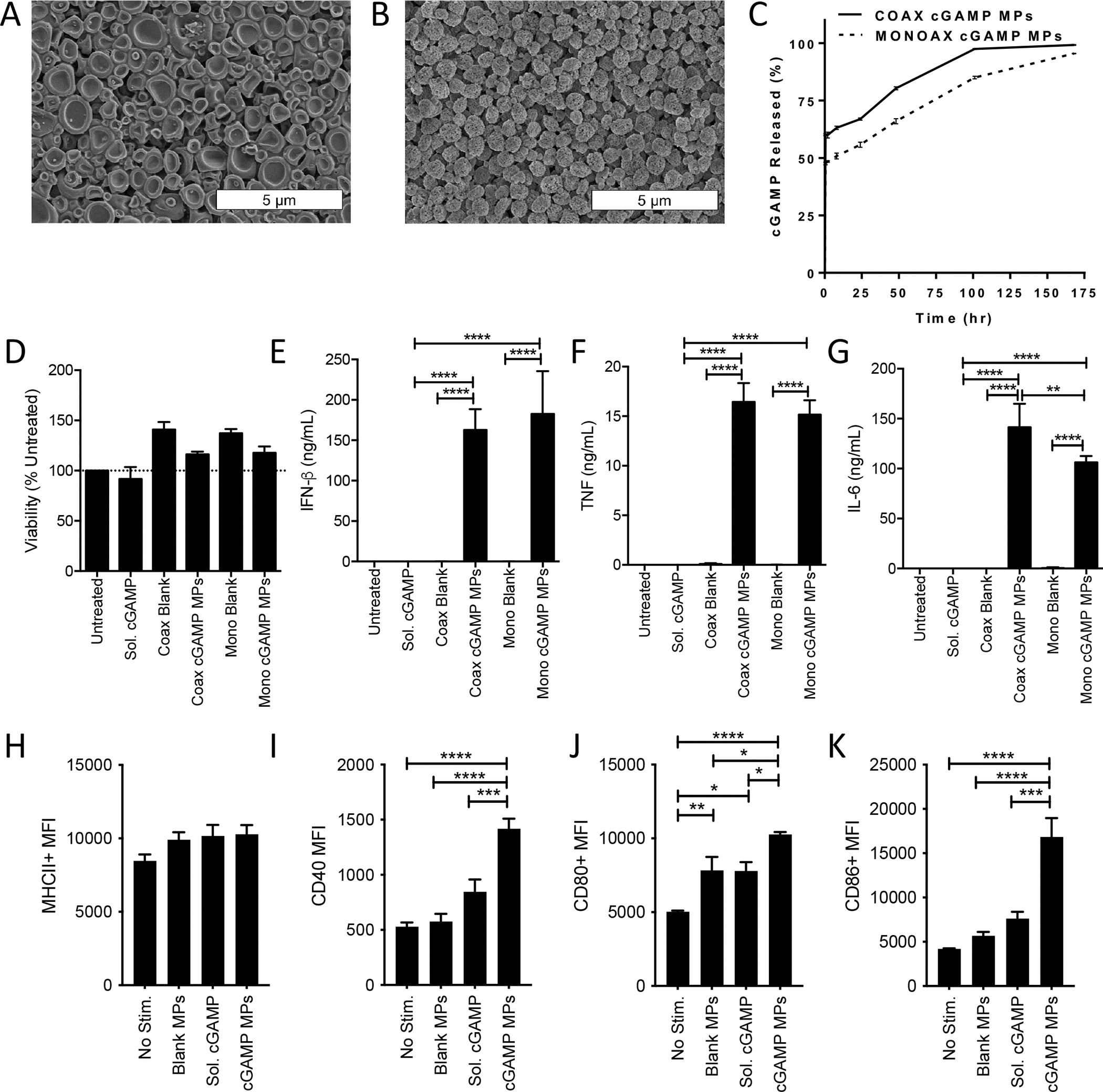
(A-B) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images were taken of cGAMP MPs made by (A) coaxial (coax) or (B) monoaxial (mono) electrospray. (C) Percent of free cGAMP released into solution from the initial calculated cGAMP encapsulated within coaxial (solid line) and monoaxial (segmented line) MPs while incubated at 37 °C and pH 7.4 (n=3 ± SD). (D-K) Bone marrow derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) from C57BL/6 mice were treated with 1 μg/mL cGAMP delivered as soluble CDN or encapsulated within Ace-DEX cGAMP MPs at a loading of 10 μg/mg MP through coaxial or monoaxial electrospray. Empty particle controls were also tested. (D-G) Twenty-four hours later cell supernatants were collected and assayed for (D) viability (E) IFN-β, (F) TNF, or (G) IL-6. (n=3 ± SEM). (H-K) Forty-eight hours later, flow cytometry was used to analyze upregulation of surface activation markers of antigen presenting cells including (H) MHCII, (I) CD40, (J) CD80, and (K) CD86. (n=6 ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p < 0.0001).
