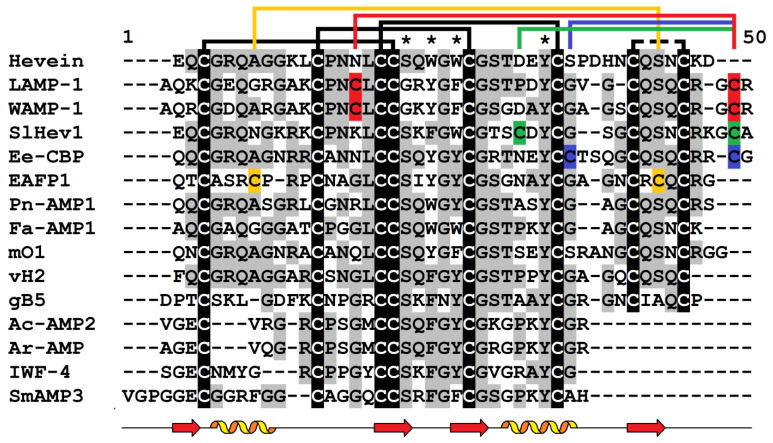
Figure 3.
Multiple sequence alignment of hevein (UniProt P02877.2) and selected hevein-like AMPs: LAMP-1 (UniProt P86521.2) from Leymus arenarius and WAMP-1 (UniProt P85966.2) from Triticum kiharae; SlHev1 (GenBank UXX20393.1) from Solanum lycopersicum; Ee-CBP1 (GenBank AAP35269.1) from Euonymus europaeus; EAFP1 from Eucommia ulmoides (UniProt P83596.1); Pn-AMP1 from Pharbitis nil (UniProt P81591.1); Fa-AMP1 from Fagopyrum esculentum (UniProt P0DKH7.1); mO1 (UniProt A0A1S6EK91.1) from Moringa oleifera; vH2 from Vaccaria hispanica (PDB 5XDI); gB1 from Ginkgo biloba [53]; Ac-AMP2 from Amaranthus caudatus (GenBank AAB22102); Ar-AMP from A. retroflexus (UniProt Q5I2B2.1); IWF-4 from Beta vulgaris [55]; and SmAMP3 from Stellaria media (UniProt C0HJU5.1). Conserved cysteine residues are highlighted in white on a black background. The cysteine residues involved in the formation of the 5th disulfide bond are shown by red color for WAMP-1 and LAMP-1, by green color for SlHev1, and by blue color for Ee-CBP. Conserved amino acid residues are highlighted in black on the grey background. Lines above the sequences denote disulfide bonds. Asterisks indicate conserved amino acid residues of the chitin-binding site. Secondary structure elements (α- and 310-heliсеs, and β-strands) for WAMP-1 (PDB 2LB7) are shown under the alignment as helices and arrows, respectively.