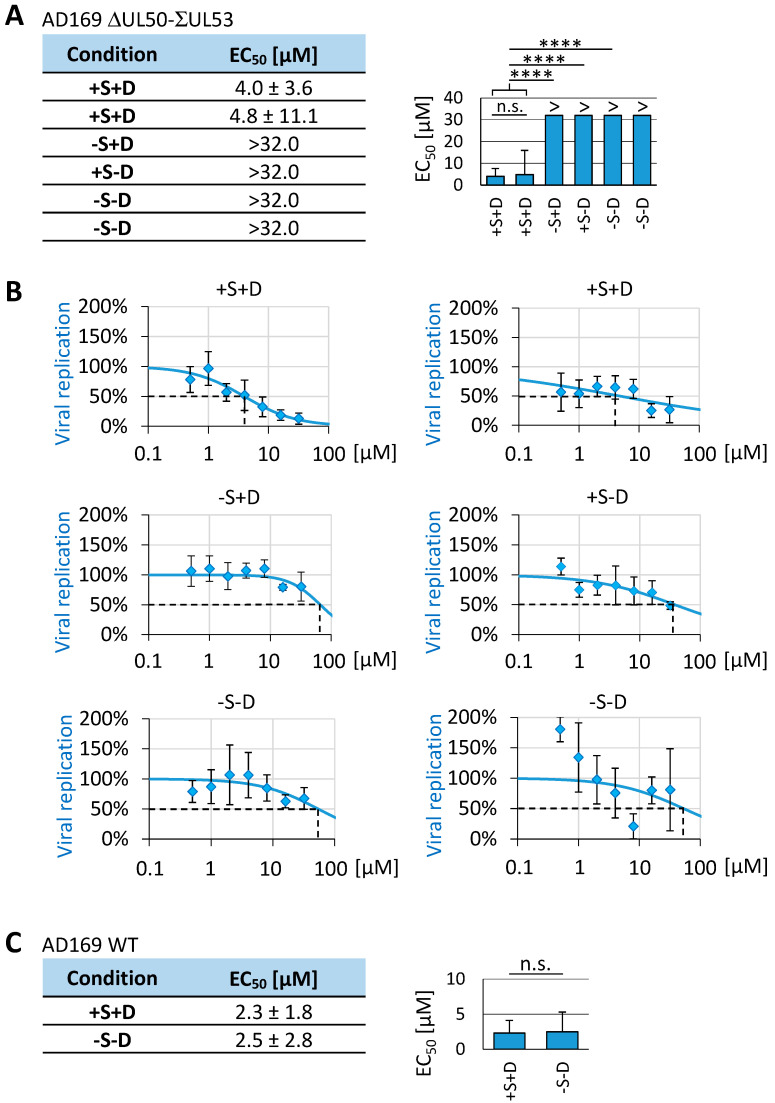
Figure 16.
Loss of antiviral efficacy of ibrutinib in HCMV ∆UL50-ΣUL53-infected cells under conditions that did not allow the expression of viral core NEC proteins as a drug target. HFF-UL50 cells were cultivated in 96-well plates and infected with (A,B) HCMV ∆UL50-ΣUL53, with (C) parental HCMV AD169 (WT), using adjusted genome copy numbers, or remained uninfected (mock). Viral input was adjusted to 1 × 105 copies per well. Infected cells were treated with a serial concentration of ibrutinib ranging from 0.5 µM to 50.0 µM. Infected and treated cells were maintained under variable conditions, including the indicated combinations of Shield-1 (±Shield-1, 1 µM) and Dox (±Dox, 500 ng/mL) addition. Dox was refreshed every second day. At 14 d p.i., supernatants were harvested, and viral genome equivalents were determined using HCMV IE1-specific qPCR. Each condition was examined in biological quadruplicates; mean values ± SDs are shown. In addition, the conditions, +S + D and −S −D, were given by two independent experimental replicates (whereby the second −S −D setting (panel B, lower right) had the highest SD and was excluded from statistics shown in panel (A)). Statistical analysis was performed using ordinary one-way ANOVA and post hoc Tukey testing; **** p ≤ 0.0001; n.s., not significant.