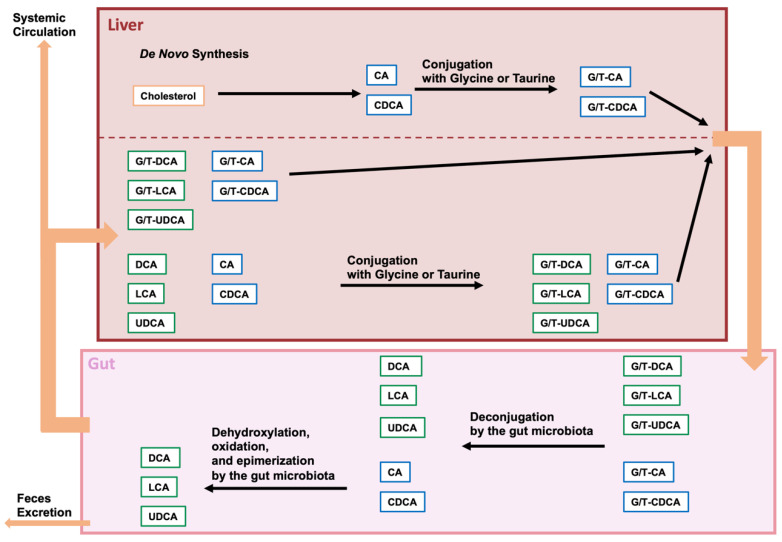
Figure 1.
Modification of bile acids by the gut microbiome. Cholesterol is converted in the liver to cholic acid (CA) or chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), and these bile acids are then con-jugated with glycine or taurine (G/T). Conjugated CA and CDCA are transferred to the gallbladder and secreted from the gallbladder into the intestine upon food intake. Conjugated BA is deconjugated by intestinal bacterial bile salt hydrolases (BSHs), and CA and CDCA are further dehydrogenated to deoxycholic acid (DCA) and lithocholic acid (LCA), respectively. CDCA is also dehydrogenated and epimerized by intestinal bacteria and converted to ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA). Approximately 95% of the BAs in the gut are absorbed and transferred to the liver, while the remaining BAs are excreted in the feces. Some of the BAs reabsorbed from the gut are effluxed into the systemic circulation.