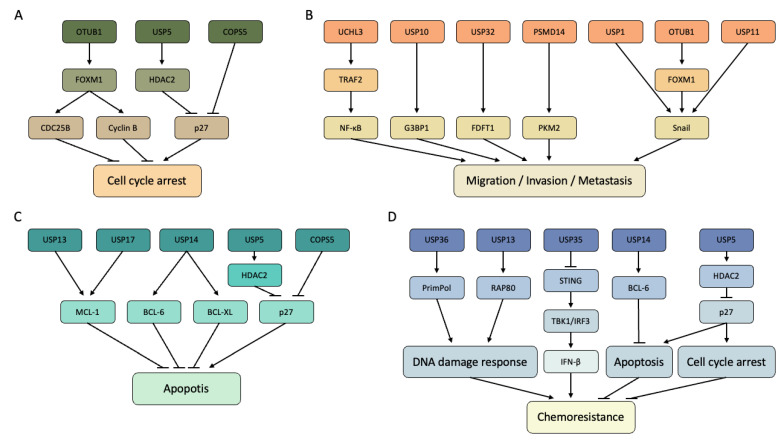
Figure 2.
DUBs, substrates, and their functions. (A) DUBs and substrates associated with cell cycle arrest. (B) DUBs and substrates associated with migration, invasion, and metastasis. (C) DUBs and substrates associated with apoptosis. (D) DUBs and substrates associated with DNA damage response and chemoresistance. The arrows from the DUBs to the substrates indicate that the binding between them is confirmed, and the stability of the substrate is controlled by DUBs.