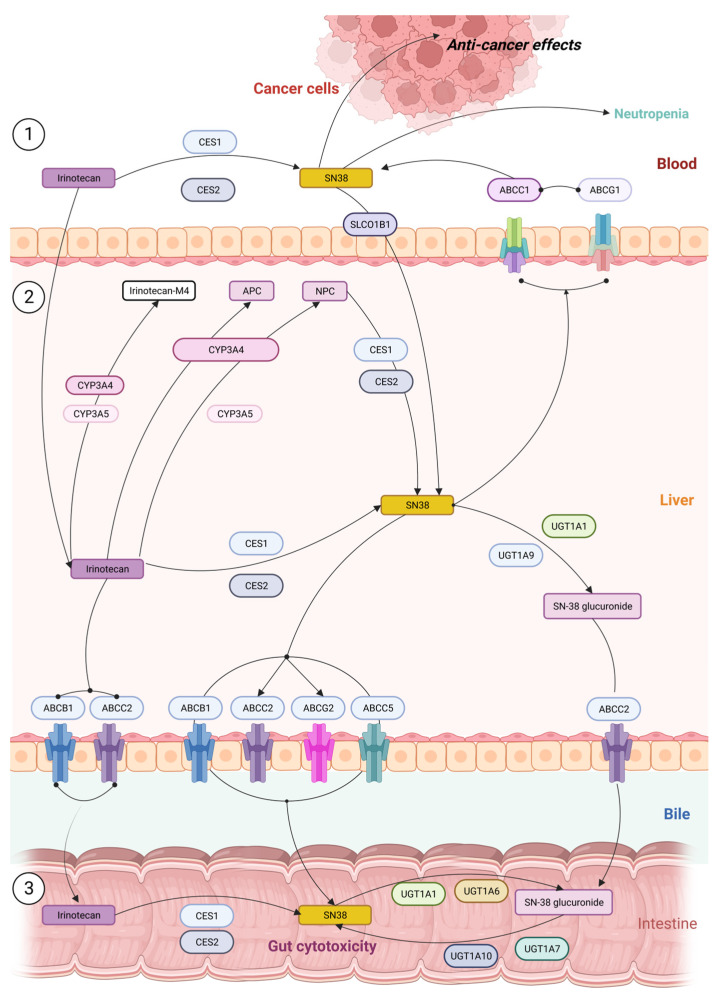
Figure 2.
Pathways of irinotecan metabolism in the liver cells ① showing the conversion of inactive form to active SN-38 leading to neutropenia; ② the drug enters via ABC transporters where it is converted to derivatives irinotecan M4, APC, and NPC; ③ the excreted version of irinotecan or SN38G is reconverted to active form SN-38 in intestine and causes GI toxicity.