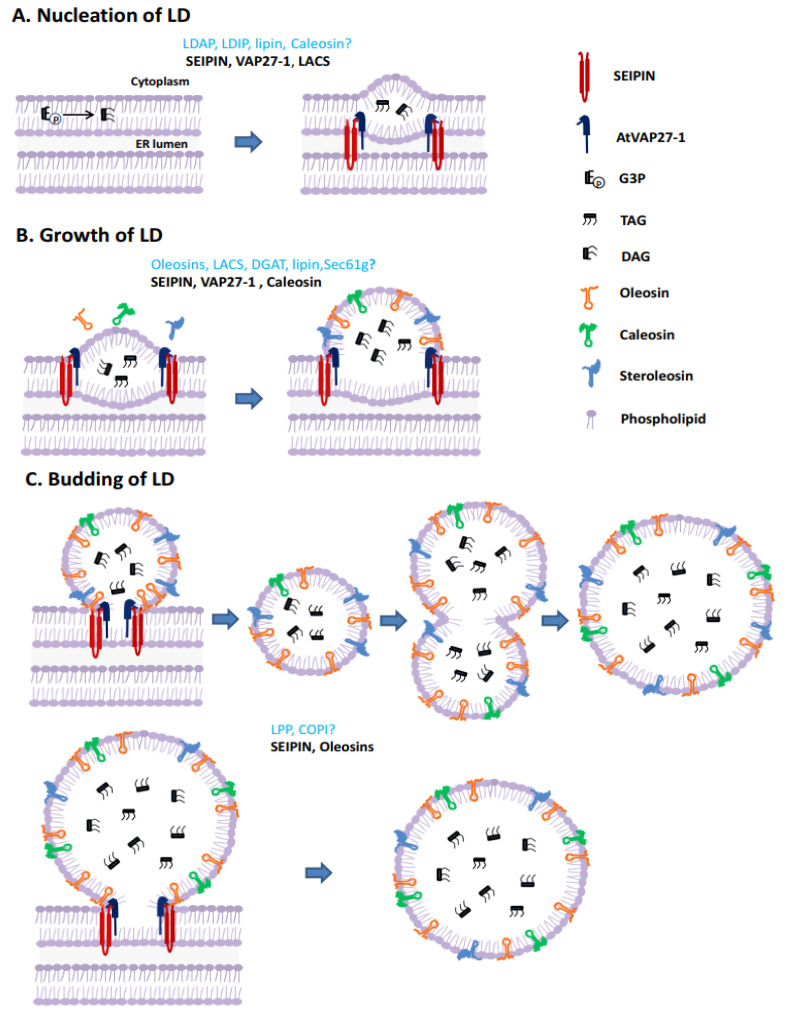
Figure 1.
Models of lipid droplet biogenesis in plant (using LDs in seeds as an example). (A) Nucleation of LD. Neutral lipids (mainly TAG) nucleate and a lens-like structure is formed in the ER membrane. (B) Growth of LD. LD-specific proteins synthesized in the cytoplasm migrate toward sites of TAG accumulation and are inserted into the ER. The size of the neutral lipid core increases and protrudes due to the accumulation of TAG. (C) LD budding. After reaching a critical size, a nearly globular LD surrounded by an ER monolayer is formed and then splits from the mother membrane. Alternatively, nascent small LDs fuse to form large ones after budding.