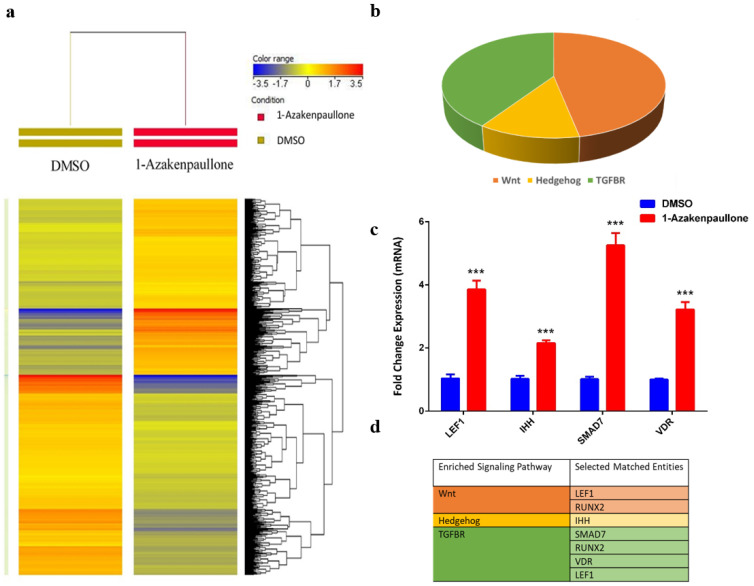
Figure 3.
1-Azakenpaullon enhances expression of multiple signaling pathways in human MSCs during osteoblastic differentiation. (a) Heat map and unsupervised hierarchical clustering performed on differentially expressed genes during osteoblastic differentiation of 1-Azakenpaullon-treated human MSCs versus DMSO-treated control cells. (b) Pie chart demonstrating the distribution of selected signaling pathways enriched in the significantly upregulated genes identified in 1-Azakenpaullon-treated human MSCs versus DMSO-treated control cells. (c) Validation of a selected panel of upregulated genes in 1-Azakenpaullon-treated human MSCs versus DMSO-treated control using qRT-PCR. Gene expression was normalized to GAPDH. Data are presented as mean fold change ± SEM (n = 6) from two independent experiments; *** p < 0.0001. (d) Selected matched entities associated with the validated signaling pathways enriched in the significantly upregulated genes identified in 1-Azakenpaullon-treated human MSCs versus DMSO-treated control cells. Gene expression was normalized to GAPDH. Data are presented as mean fold change ± SEM (n = 6) from two independent experiments; *** p ≤ 0.0005. LEF1: lymphoid enhancer binding factor 1; IHH: Indian hedgehog homolog; SMAD7: mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7; VDR: vitamin D receptor; DMSO: dimethyl sulfoxide.