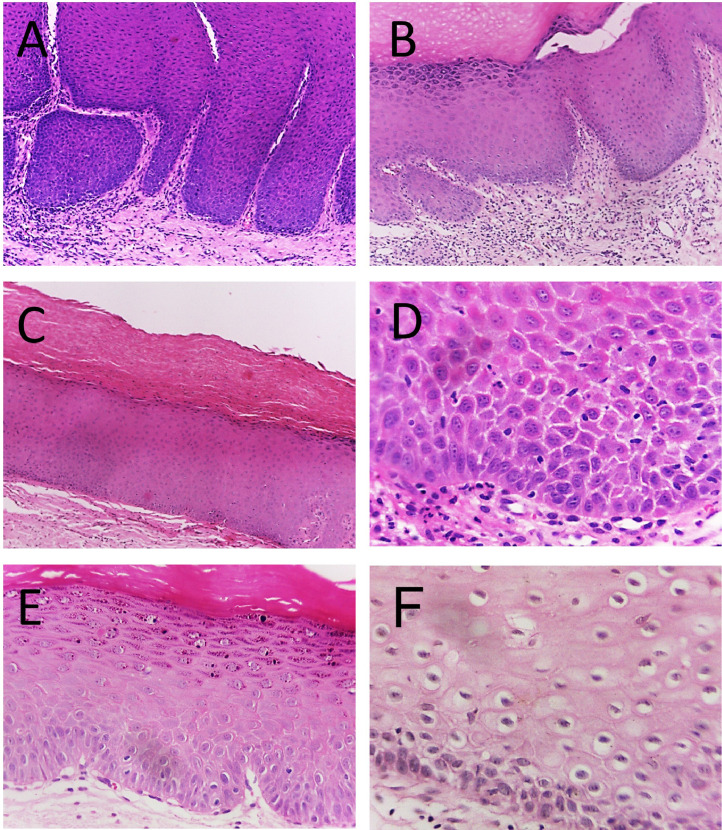
Fig. 5.
[A - C] Oral leukoplakias histopathological images obtained with the 10x objective lens of a light microscope. [A] Hyperplastic squamous epithelium is observed, showing intense acanthosis, in addition there is a subepithelial inflammatory infiltrate. [B] Evident hyperorthokeratosis, with acquisition of the granular layer and acanthosis, there are vessels and inflammatory infiltrate in the connective tissue. [C] Thick orthokeratinized layer present on the surface of the epithelium; also a flat interface with connective tissue is seen. [D - F] Histopathological images of oral leukoplakias, captured with the 40x objective lens. [D] Intercellular bridges in the epithelium, exocytosis, and mild cellular pleomorphism are observed. In the connective tissue there is lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate. [E] Hyperplastic orthokeratinized epithelium, with evident granular layer, and epithelial dysplasia in the lower third, evidenced by the presence of drop-shaped rete ridges along with nuclear and cellular pleomorphism. [F] Presence of koilocytosis.