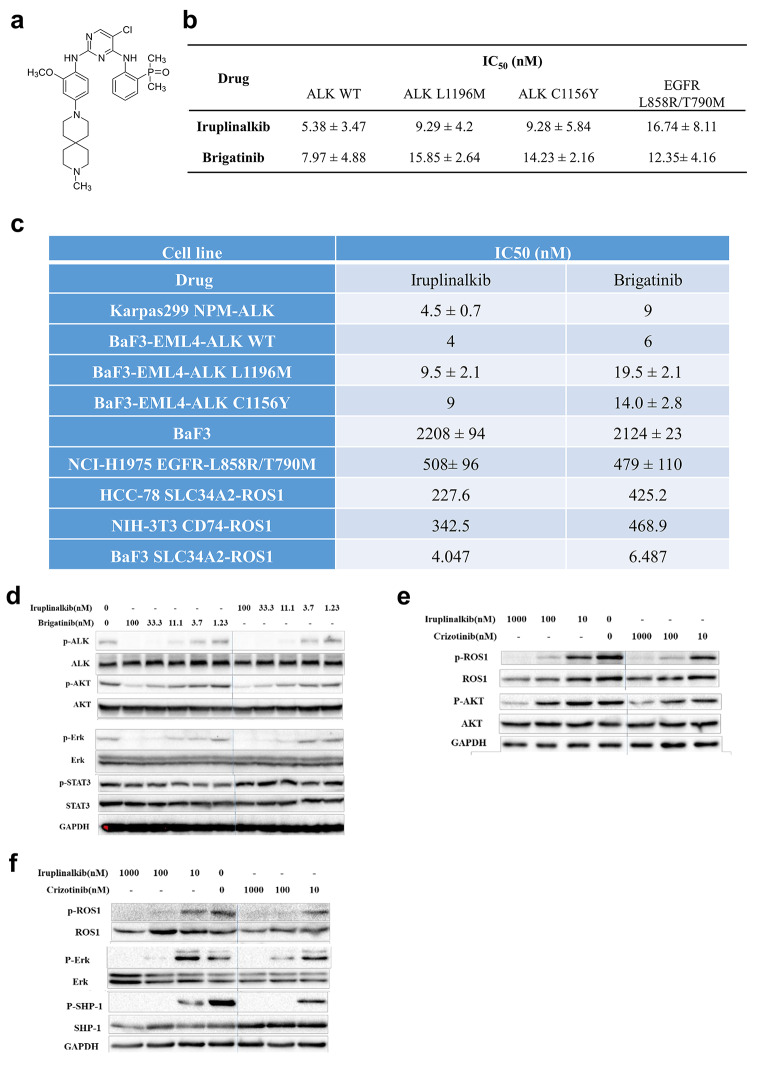
Fig. 1.
Iruplinalkib inhibited kinase activity and the downstream signaling pathways of ALK and ROS1 in vitro. (a) Chemical formula of iruplinalkib. (b) Iruplinalkib and brigatinib inhibited the kinase activity of ALKWT, ALKL1196M, ALKC1156Y, and EGFRL858R/T790M. (c) The kinase selectivity of iruplinalkib and brigatinib to the fusion protein. Proliferation of Karpas299 (NPM-ALK), Ba/F3, Ba/F3 (EML4-ALKWT), Ba/F3 (EML4-ALKL1196M), Ba/F3 (EML4-ALKC1156Y), NCI-H1975 (EGFRL858R/T790M), HCC-78 (SLC34A2-ROS1), NIH-3T3 (CD74-ROS1), and Ba/F3 (SLC34A2-ROS1) cells. (d) The inhibitory effects of iruplinalkib on the phosphorylation of ALK, PI3K/AKT, RAS/MAPK and JAK/STAT3 pathways in NCI-H3122 cells, respectively. (e) Iruplinalkib inhibited phosphorylation of ROS1, PI3K/AKT and RAS/MAPK pathways in NIH-3T3 cells stably expressing CD74-ROS1, respectively. (f) Iruplinalkib inhibited phosphorylation of ROS1, RAS/MAPK and SHP-1 pathways in Ba/F3 cells stably expressing SLC34A2-ROS1, respectively