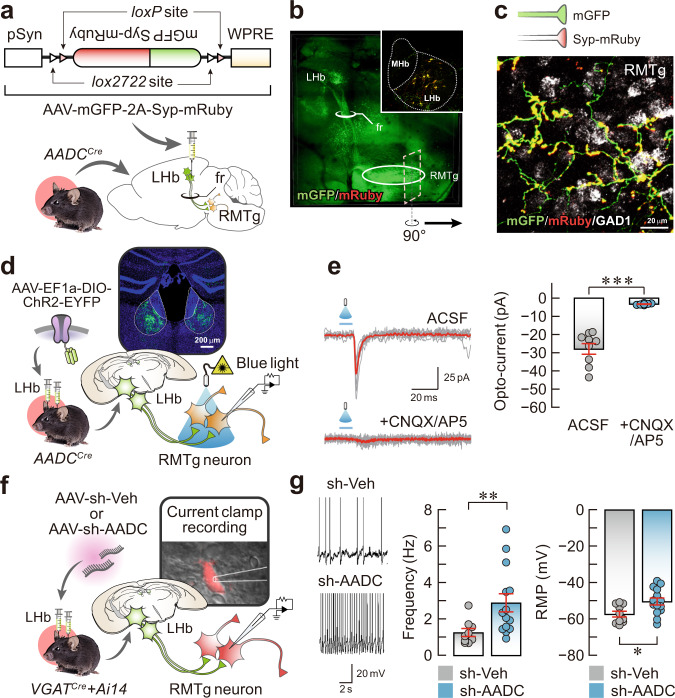
Fig. 4. LHb D-neurons innervate RMTg GABAergic neurons.
a Schematic of the AAV used and experimental procedure for anterograde tracing. b Representative AAV-hSyn-mGFP-Syp-mRuby infection pattern in the LHb (inset) and the sagittal fluorescent image showing LHb D-neuron projections. c, A rotated and magnified image of the region of interest (dashed square) from (b). LHb D-neuronal terminals on GABAergic neurons of the RMTg were detected by FISH. d Schematic of AAV-ChR2 injection into the LHb and the response of RMTg GABAergic neurons to brief optical stimulation. e Traces from oEPSCs (left) and summary data on normalised oEPSC amplitude under baseline conditions after CNQX (20 μM) and AP5 (50 μM) perfusion in ACSF (right) (n = 9 cells from independent ChR2 mice). f Schematic of the method for measuring the firing rate of RMTg GABAergic neurons in AADC-knockdown VGATCre::Ai14 mice and their vehicle controls. g Representative traces (left), firing frequency (middle; n = 9 cells from independent sh-Veh mice and n = 14 cells from independent sh-AADC mice) and RMP (right; n = 10 cells from independent sh-Veh mice and n = 14 cells from independent sh-AADC mice). Unless otherwise stated, statistical comparisons were performed using a two-tailed unpaired t test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001. Data are presented as the mean values ± s.e.m. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.