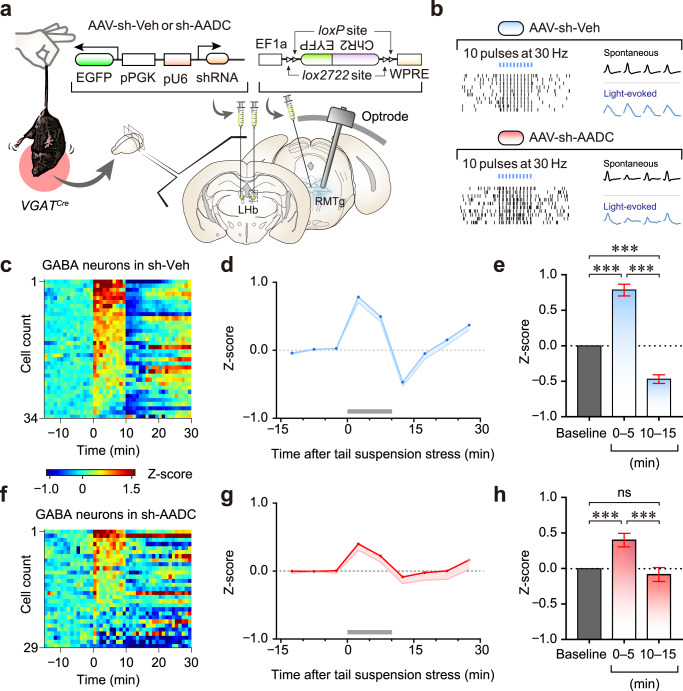
Fig. 6. LHb D-neurons regulate RMTg GABAergic responses to acute stress through trace aminergic signalling.
a Schematic of in vivo recording of RMTg GABAergic neuronal activity under tail suspension stress. b Optical identification of ChR2-expressing GABAergic neurons in the RMTg. The raster plots of two representative GABAergic neurons from control and AADC-knockdown mice. c, f Heatmaps of the average normalised firing of GABA neurons (5-min bins) in control (c) and AADC-knockdown (f) mice. Tail suspension stress was given for 10 min from time 0. d, g Normalised firing rates of all GABAergic neurons in control (d) and AADC-knockdown (g) mice. Tail suspension stress is shown as grey bars in (d) and (g). e, h Comparisons of average firing rates before (baseline), during (0–5 min) and after (10–15 min) tail suspension in control (n = 34 cells from independent sh-Veh mice) (e) and AADC-knockdown (n = 29 cells from independent sh-AADC mice) (h) mice. Unless otherwise stated, statistical comparisons were performed using repeated measure one-way ANOVA followed by contrast test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001. Data are presented as the mean values ± s.e.m. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.