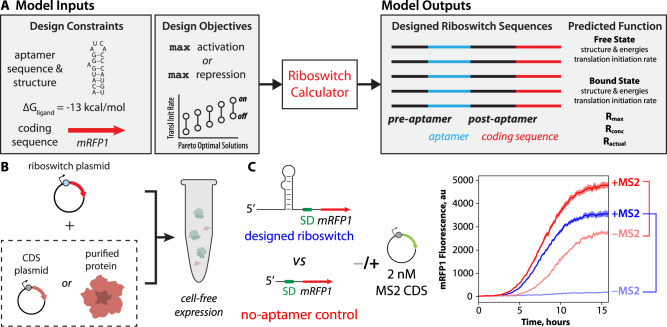
Fig. 1. Design of protein-sensing riboswitches and cell-free riboswitch characterization.
A A model of translation-regulating riboswitches takes as inputs the sequence, structure, and binding free energy of a protein-binding RNA aptamer. The model designs candidate riboswitch sequences that maximize activation or repression of translation initiation in response to changing protein concentrations. B The riboswitch sensor is tested in a cell-free expression system (TX-TL), adding either protein expression plasmid or purified protein. C Riboswitch sensor function is characterized by measuring reporter protein expression levels in response to changing protein-ligand concentrations alongside the same measurements on a no-aptamer control. The riboswitch activation or repression ratio is determined by comparing reporter expression levels, including the no-aptamer control measurements, to exclude non-specific interactions. Example cell-free assay measurements include (light blue), an MS2-sensing riboswitch without added MS2 protein; (dark blue) an MS2-sensing riboswitch with added MS2 expression plasmid; (light red) the no-aptamer control without added MS2 protein; and (dark red) the no-aptamer control with added MS2 expression plasmid. Lines are the mean mRFP1 fluorescence levels at each time point. Shaded regions are the 95% confidence interval at each time point (N = 6 biological replicates).