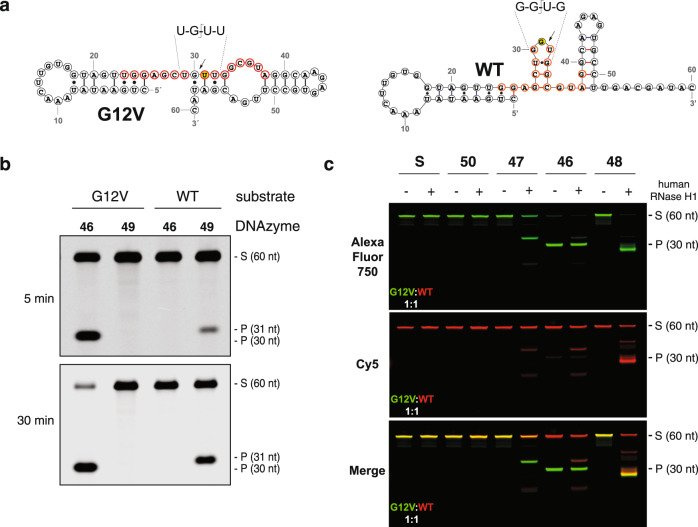
Fig. 4. Allele-specific targeting of wild-type and KRAS G12V RNA under cell-free conditions.
a Substrates used to evaluate allele-specific RNA cleavage of KRAS G12V include two 60 nt segments of KRAS mRNA that differ by a single point mutation. The G12V version carries a G-to-U mutation (yellow) that leads to a glycine-to-valine mutation in the translated KRAS protein. RNA binding sites targeted by the wild-type (49) and G12V (46)-specific DNAzymes of Dz 10-23_v46 are shown in red, with the cleavage site indicated with an arrow. b Denaturing PAGE gel showing allele-specific RNA cleavage of both alleles by the wild-type (49) and G12V (46)-specific DNAzymes after 5 and 30 min (n = 3). Reactions were performed in a buffer containing 1 mM MgCl2, 50 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 10 mM NaCl, and 140 mM KCl at 37 °C with 500 nM substrate and 50 nM enzyme (10:1, S:E). S: 5′-Cy5-labeled full-length substrate, P: 5′-Cy5-labeled cleavage product. c Denaturing PAGE gel showing RNA cleavage profiles in reactions containing both the wild-type (red) and G12V (green) substrates (1:1) in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 5 ng/μL human RNase H1 after a 30-min incubation (n = 1). Individual Cy5 (red) and AlexaFluor750 (green) channels, as well as the merged image, are shown. Reactions were performed using unpaired Dz (50), inactive Dz (47), active G12V Dz (46), and 22 nt linear DNA control (48) in buffer containing 1 mM MgCl2, 50 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 10 mM NaCl, and 140 mM KCl at 37 °C with 250 nM total substrate and 250 nM enzyme. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.