Figure 5.
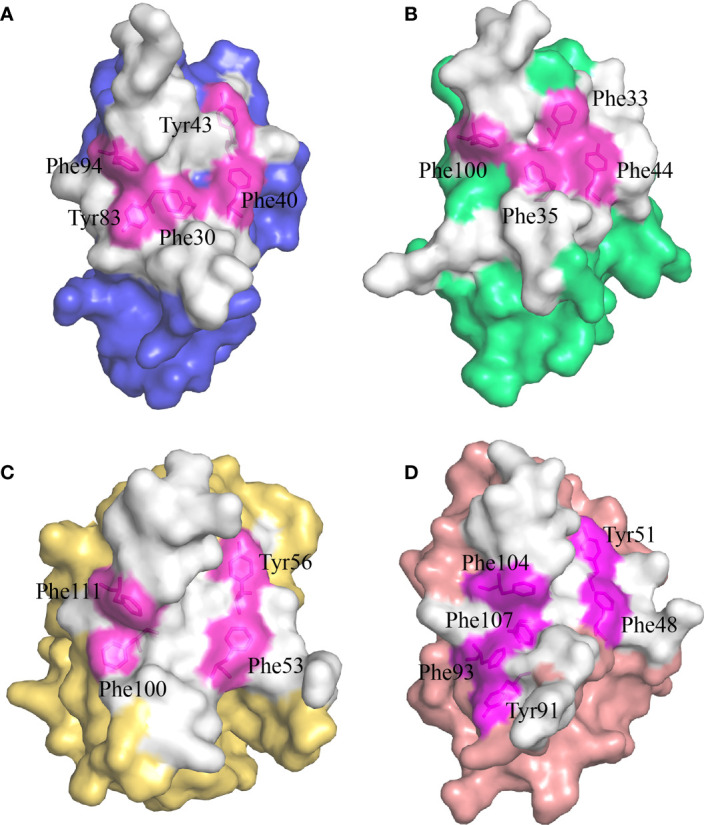
The hydrophobic core of the CD8αα homodimer in small-spotted catshark compared to other vertebrate species. The surface of each CD8α monomer is rendered in a different color while residues forming the hydrophobic core are shown in stick representation and surface rendered in magenta. (A) The hydrophobic core of ScCD8αα is formed by five hydrophobic residues (Phe30, Tyr43, Phe40, Tyr83 and Phe94). (B) The hydrophobic core of grass carp CD8αα is formed by four hydrophobic residues (Phe32, Phe35, Tyr44, and Phe100). (C) The hydrophobic core of chicken CD8αα is formed by four hydrophobic residues (Phe53, Tyr56, Phe100, and Phe111). (D) The hydrophobic core of human CD8αα is formed by six hydrophobic residues (Phe48, Tyr51, Tyr91, Phe93, Phe104 and Phe107).
