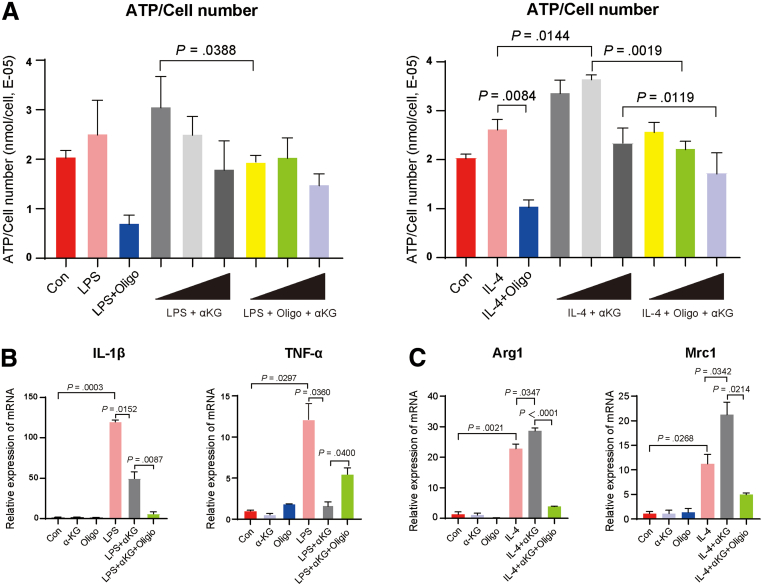
Figure 9.
Exogenous αKG supplement could promote BMDM M2 activation and inhibit M1 polarization. (A) On the left, the value of ATP production normalized by cell number of M1 macrophage-related group: Con, LPS stimulation group, LPS + oligomycin A group, LPS + dose gradient of αKG (0.1, 1, 10 μmol/L), and LPS + oligomycin A + dose gradient of αKG (0.1, 1, 10 μmol/L) (n = 3). On the right, the value of ATP normalized by cell number of M2 macrophage-related group: Con, IL-4 stimulation, IL-4 + oligomycin A, IL-4 + dose gradient of αKG (0.1, 1, 10 μmol/L), and IL-4 + oligomycin A + dose gradient of αKG (0.1, 1, 10 μmol/L) (n = 3). After 1 μmol/L of αKG was chosen as the optimal concentration to increase ATP production of BMDMs, M1 and M2 markers were used to perform macrophage phenotyping by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. (B) Relative mRNA expression of the M1 marker genes Il1β, Tnfα in LPS induced-M1 macrophage related group. (C) Relative mRNA expression of the M2 marker genes Arg1, Mrc1 in IL-4 induced-M2 macrophage related group. For all data, statistical comparisons between 2 groups were carried out by Student t test. P < .05 indicates significant differences. LPS, lipopolysaccharide.