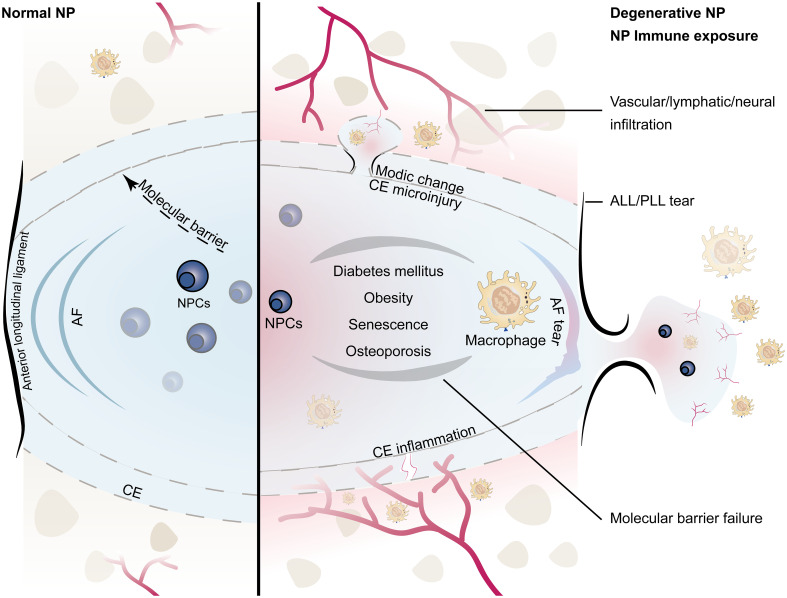
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the immune barrier of the NP (left): including the AF, the upper and lower CE, the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments, and the molecular immune barrier; microvessels are distributed around the NP without infiltration; the height of the NP is normal. NP immune exposure and NP-macrophage interaction (right): including CE damage, AF rupture, ALL/PLL rupture, and failure of the molecular immune barrier, which are mostly related to intervertebral disc injury caused by abnormal stress; immunogenicity of the NP induces macrophage infiltration; microinjury may lead to Modic changes, while severe injury tends to induce endplate chondritis; the height of the NP decreases; the number of NPCs decreases. (NP, nucleus pulposus; NPCs, nucleus pulposus cells; CE, cartilage endplate; AF, annulus fibrosus; ALL/PLL, anterior longitudinal ligament/posterior longitudinal ligament).