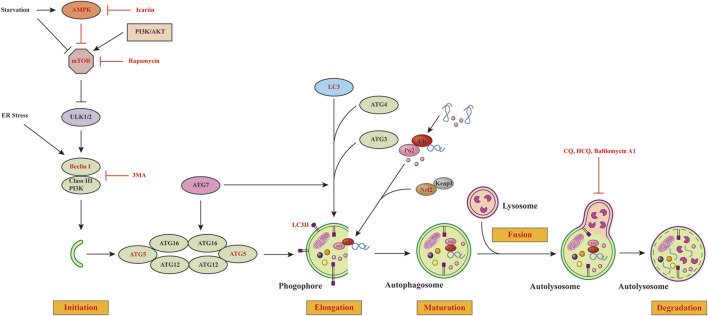
FIGURE 1.
Major regulatory signaling pathways of autophagy. Autophagy is a process consisting of initiation, elongation, maturation and degradation steps. The PI3K-AKT pathway is the upstream activator of mTORC1, whereas AMPK initiates autophagy by inhibiting the mTORC1 activity or directly activating the ULK1/2 complex. mTORC1 activation inhibits autophagy by inhibiting the ULK1/2 complex, which is necessary for the induction of autophagy. When activating the ULK1/2 complex, it can recruit Beclin 1/III class PI3K complexes to the site of autophagosome formation. LC3-II exerts an essential role in the formation of autophagosome through binding to the autophagosomal membrane. P62 can serve as a connection between LC3 and ubiquitinated proteins. Autophagosome fuses with lysosome to form autolysosome. Eventually, autolysosome is degraded by lysosomal enzymes. We have highlighted in red the autophagic steps linked to inflammation, adipogenesis and HA accumulation in GO that have been discussed in this review. mTORC1, Rapamycin complex 1; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; rapamycin (mTOR) kinase; AMPK, AMP-dependent protein kinase; PI3K-AKT pathway, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)–protein kinase B (AKT) pathway; ULK1/2 complex, UNC-51–like kinase1 or 2; LC3, light chain 3 protein; ATG, autophagy related genes; CQ, Chloroquine; HCQ, hydroxychloroquine.