Figure 1.
A kinome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screen identifies CK1α as a therapeutic target to overcome ENZA resistance
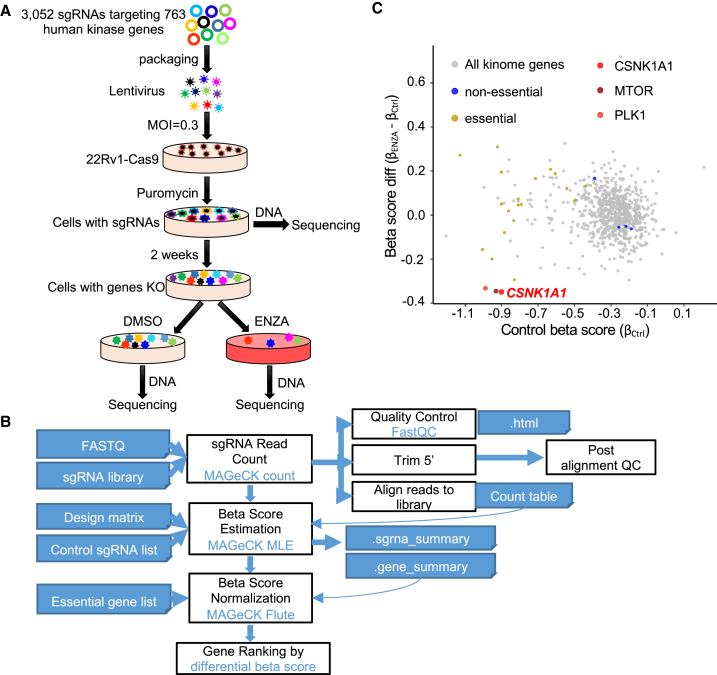
(A) Workflow of the kinome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screen. MOI, multiplicity of infection; 22Rv1-Cas9, 22Rv1 cell line stably expressing Cas9.
(B) Workflow of CRISPR screen data analysis with MAGeCK.
(C) Scatterplot showing gene differential beta score (subtracting the control beta score from the treatment beta score) versus gene beta score in control samples. CSNK1A1, MTOR, and PLK1 are the top three negatively selected genes that mediated sensitivity to ENZA. Genes in the kinome library that overlap with essential genes and non-essential genes, reported previously, are highlighted in yellow and blue, respectively.