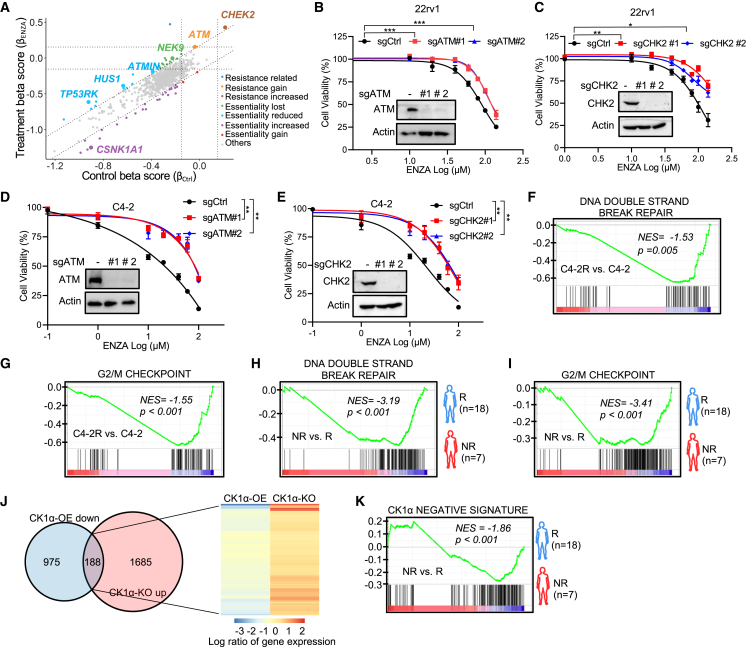
Figure 4.
DSB signaling is involved in ENZA resistance
(A) Scatterplot showing gene beta score of ENZA treatment versus gene beta score in control samples. Resistance or essentiality related genes are highlighted as indicated.
(B–E) In vitro proliferation of 22Rv1 cells (B and C) or C4-2 cells (D and E) expressing sgCtrl or two sgRNAs against ATM (B and D) or CHK2 (C and E) was determined by AquaBluer assay after treatment for 72 h with the indicated concentrations of ENZA. Insets are IB results of WCL of 22Rv1 cells (B and C) or C4-2 cells (D and E) expressing sgCtrl or two sgRNAs against ATM (B and D) or CHK2 (C and E).
(F–I) GSEA showing the enrichment of G2/M checkpoint and DNA DSB repair gene sets in the indicated groups, C4-2R versus C4-2 (F and G), non-responder (NR) to ENZA versus responder (R) (dataset from the study described by Alumkal et al.7) (H and I).
(J) Venn diagram showing genes that are downregulated in 22Rv1 cells after CK1α overexpression (OE) compared with the control or genes that are upregulated in 22Rv1 cells with CK1α knockout (KO) compared with the control. Heatmap showing expression of the overlapped genes.
(K) GSEA showing the enrichment of “CK1α negative signature” in NR to ENZA versus R (dataset from the study described by Alumkal et al.7).