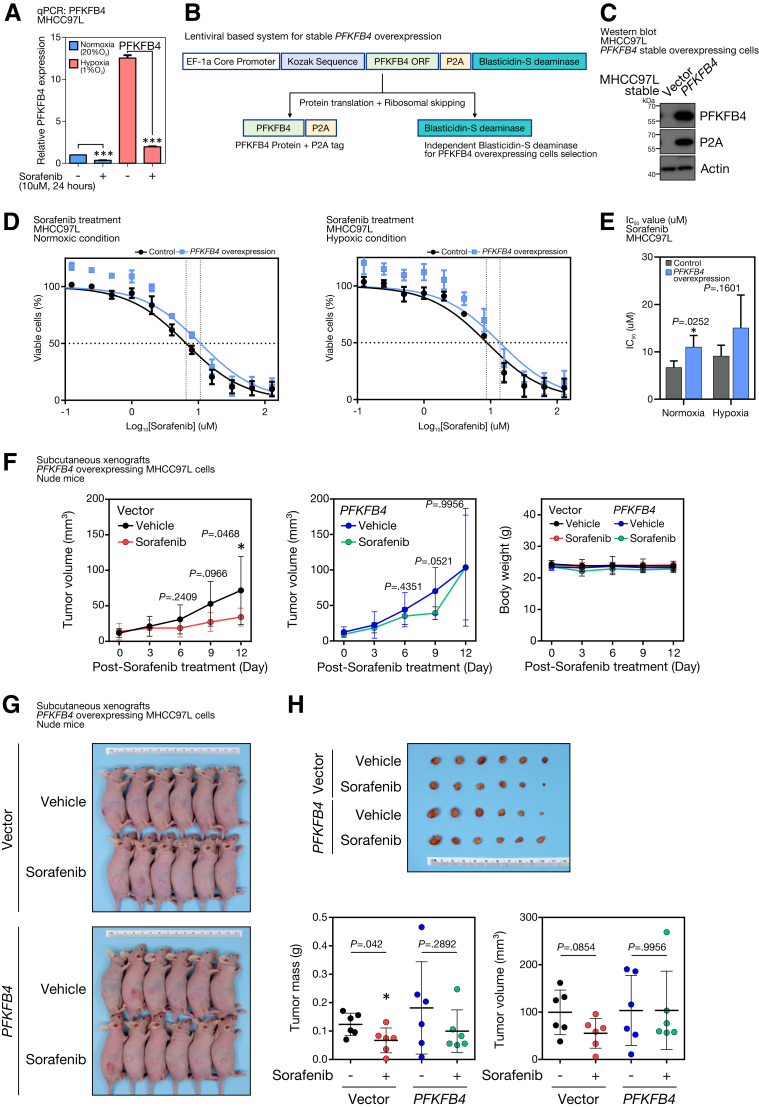
Figure 8.
Ectopic PFKFB4 expression promoted sorafenib resistance to HCC cells. (A) PFKFB4 transcript expression in sorafenib-treated MHCC97L cells under normoxic (20% O2) and hypoxic (1% O2) conditions. (B) Schematic diagram illustrating the lentiviral-based bicistronic system that drives PFKFB4 overexpression. (C) Western blot analysis for PFKFB4 in PFKFB4-overexpressing and control MHCC97L cells. (D) Dosage response curves of sorafenib in PFKFB4-overexpressing and control MHCC97L cells under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. (E) Half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of sorafenib (umol/L ± SD) in PFKFB4-overexpressing and control MHCC97L cells. (F) Vector and PFKFB4-overexpressing MHCC97L cells, respectively, were injected subcutaneously into immunodeficient nude mice. At 2 weeks postinjection, the tumor-bearing mice were subjected to vehicle or sorafenib (5 mg/kg) treatment by daily oral gavage. The tumor volume and body weight were monitored and compared as indicated. (G) On day 12 post-treatment, the mice were killed, and the tumors in all the test groups were dissected. (H) The dissected tumor volume and tumor mass between the vehicle and sorafenib treatment groups were measured and compared. ∗P < .05 and ∗∗∗P < .001. EF-1a, Elongation factor 1-alpha.