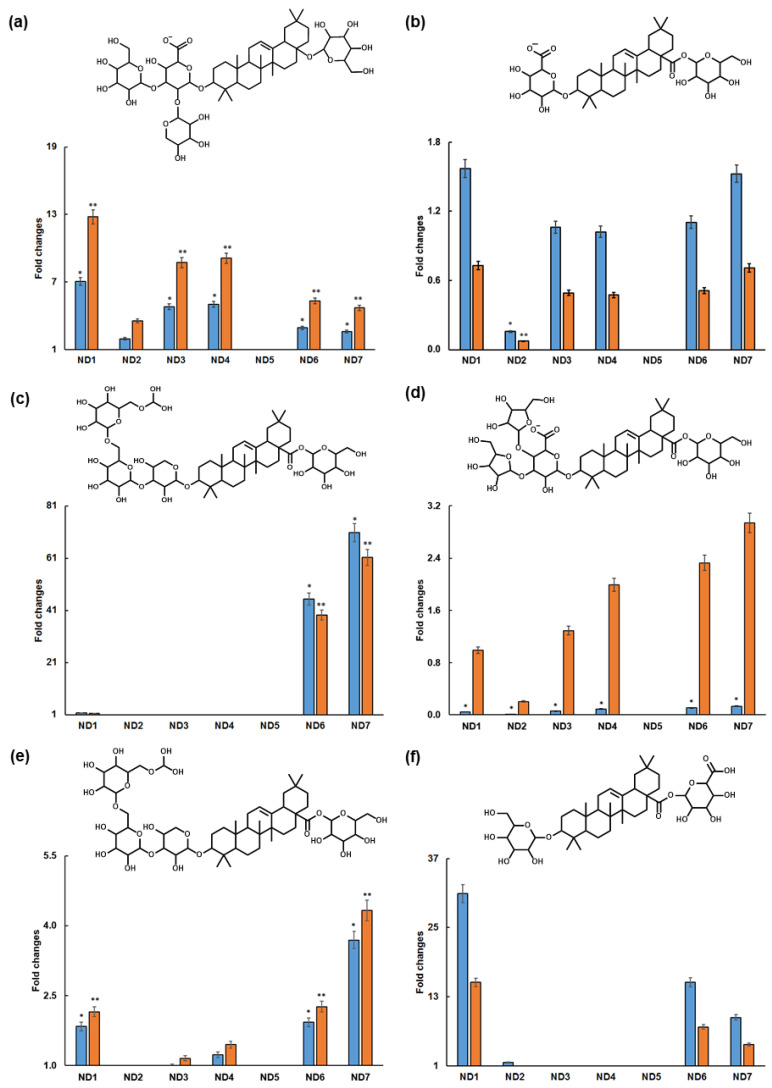
Figure 2.
Structures and relative recoveries of 6 (kalopanax–saponin F isomer 2, (a)), 7 (calendulaglycoside C isomer 1, (b)), 9 (oleanolic acid-3-O-(methyldioxy-trihexopyranosyl-1-3-pentopyranosyl)-28-1-hexopyranosyl ester, (c)), 10 (araloside (b,d)), 12 (oleanolic acid-3-O-(hexosyl)-28-1-hexouronide ester isomer 1, (e)) and 13 (calendulaglycoside C isomer 2, (f)) expressed as the ratio (fold) in comparison to those observed in aqueous (blue) and ethanolic (orange) extracts. The compounds are numbered as in Table 1. ND1—NADES based on the choline chloride–malic acid mixture (molar ratio 1:1). ND2—NADES with the molar ratio of choline chloride and malic acid of 1:2. ND3—NADES with the molar ratio of choline chloride and lactic acid of 1:3. ND4—NADES with the molar ratio of choline chloride and lactic acid of 1:3 + 30% (v/v) water. ND6—NADES with the molar ratio of sorbitol and malic acid of 1:1 + 10% (v/v) water. ND7—NADES with the molar ratio of sorbitol and malic acid of 1:2 + 20% (v/v) water. *—the difference is that the recovery of the compound is statistically significant compared to the recovery of the compound in water extract (p ≤ 0.05); **—the difference is that the recovery of the compound is statistically significant compared to the recovery of the compound in ethanol extract (p ≤ 0.05).