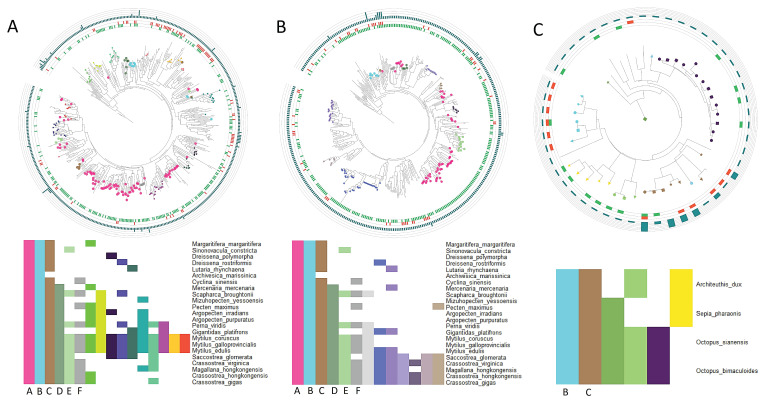
Figure 3.
C-type lectin-like (CTL) subfamilies and their conservation across mollusks in three lineage-specific repertoires. (A): Phylogenetic analysis of C-type lectin-like proteins (CTLs) in Mytilus galloprovincialis and CTL subfamilies shared by Mytilidae mussel species. CTL orthology groups shared by the three Mytilidae species are shown, along with their conservation degree at the class level among bivalves. In the phylogenetic tree, these CTL orthology subfamilies are indicated by each color. The presence of a single peptide (green bars), the presence of a transmembrane domain (orange bars), and the number of CTL domains (outer cyan bars) are indicated for each CTL protein in the phylogenetic tree. (B): Phylogenetic analysis of CTL proteins in Crassostrea gigas and CTL subfamilies shared by all Ostreidae oyster species. Distribution in the phylogenetic tree and orthology conservation of such subfamilies between bivalves is indicated. The presence of a single peptide, the presence of transmembrane domains, and the number of CTL domains are also shown. (C): Phylogenetic analysis of CTL proteins encoded in all the analyzed cephalopod species and orthology conservation of such CTLs. The presence of a single peptide, the presences of transmembrane domains, and the number of CTL domains are also shown. By comparing the orthology conservation of each lineage-specific repertoire, two orthology subfamilies conserved at the mollusk level could be identified (B, C), as well as an additional subfamily conserved between all bivalves (A). Additionally, other subfamilies were shared between the two bivalve lineage-specific repertoires of mussels and oysters (D, E, F).