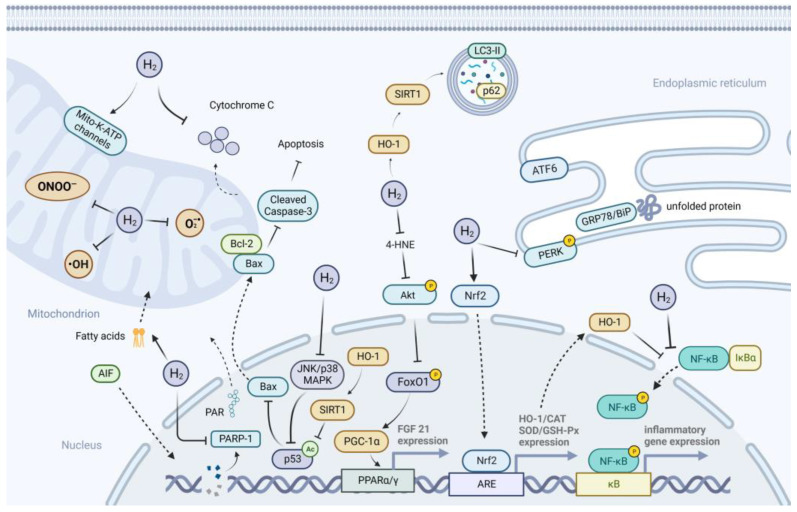
Figure 3.
The possible mechanisms underlying the effects of H2 on metabolic diseases. The figure demonstrates the potential mechanisms underlying the effects of H2 on metabolic diseases, including scavenging or inhibiting generation of ROS; activating Mito-K-ATP channels; promoting the transport of fatty acids into mitochondria; as well as the pathways involved in the anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects, and suppression of ER stress and activation of autophagy, including the Nrf2/ARE/HO-1, PARP-1/AIF, HO-1/SIRT1/p53, JNK/p38 MAPK/p53, Akt/FoxO1/PGC-1α/PPARα/γ, NF-kB-mediated, and PERK-mediated UPR pathways. Abbreviations: Mito-K-ATP, mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium; SIRT1, Sirtuin1; LC3-II, microtubule-associated protein light chain 3-II; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; ATF6, activating transcription factor 6; GRP78/BiP, glucose-regulated protein 78/binding immunoglobulin protein; PERK, proteins R (PKR)-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; 4-HNE, 4-hydoxy-2-nonenal; FoxO1, forkhead box O1; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 alpha; PPARα/γ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha/gamma; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; ARE, antioxidant responsive element; NF-kB, nuclear factor-kappaB; IkBα, inhibitory subunit of NF-kB alpha; JNK/p38 MAPK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; PARP-1, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1; PAR, poly(ADP-ribose); AIF, apoptosis-inducing factor; CAT, catalase; SOD, superoxide dismutase; GSH-Px, glutathione peroxidase; FGF21, fibroblast growth factor 21.