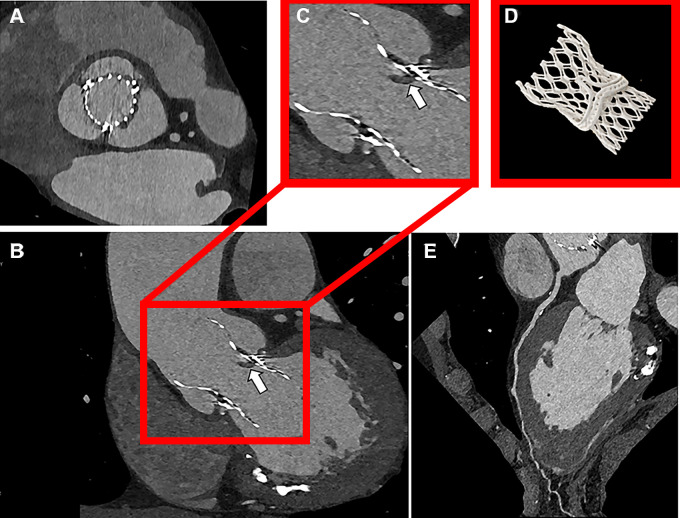
Figure 5:
Ultra-high-resolution (UHR) photon-counting detector CT images show valve-in-valve transcatheter aortic valve replacement with hypoattenuated leaflet thickening in a 72-year-old male patient scanned with contrast medium. (A) Axial UHR image (Bv56 kernel, quantum iterative reconstruction strength 4). (B) CT image shows hypoattenuating leaflet thickening (white arrow). (B, C) Surgical valve and transcatheter heart valve frames are sharply depicted in the sagittal plane. (D) Three-dimensional volume-rendered image. (E) Coronary artery calcifications in left anterior descending artery (multiplanar reformatted images).