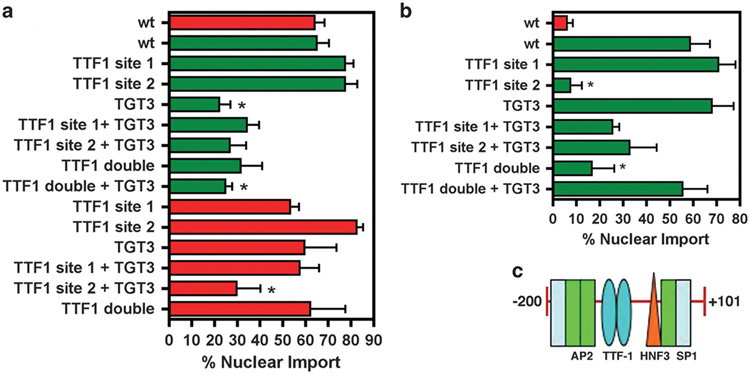
Figure 5.
Transcription-factor-binding site requirements for T1α promoter nuclear import in ATI and ATII cells. (a) Plasmids containing the wild-type 1.3 kb T1α promoter, the +101 to − 200 bp truncated promoter and promoters containing the indicated binding site mutations were cytoplasmically microinjected into D5 primary ATI cells. The localization of the plasmid was visualized by fluorescence microscopy after 5 h. The experiment was performed at least three times (mean % nuclear import±s.e.m.) with at least 50 cells counted for each condition. (b) Plasmids containing the wild-type +101 to − 200 bp truncated promoter and truncated promoters containing the indicated binding site mutations were cytoplasmically microinjected into D2 primary ATII cells. The localization of the plasmid was visualized by fluorescence microscopy after 5 h. The experiment was performed at least three times (mean % nuclear import±s.e.m.) with at least 50 cells counted for each condition. (c) The +101 to − 200 bp sequence of the T1α promoter containing binding sites for TTF-1 and HNF3. *P < 0.05 compared with full-length wild type promoter in the respective cell type.