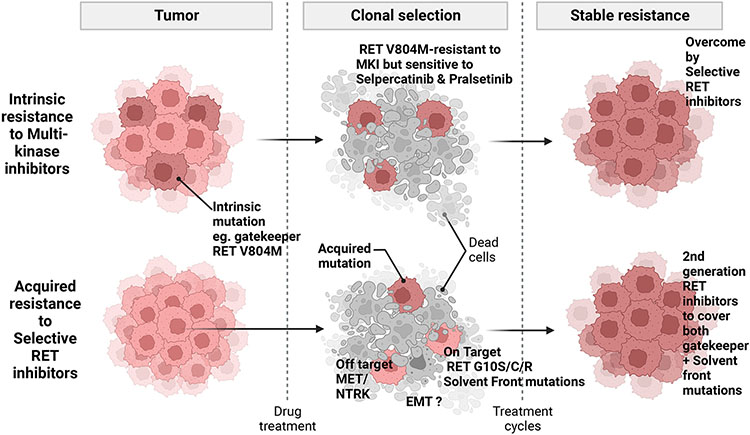
Fig. 2.
RET inhibitor resistance mechanisms. The RET V804M/L gate-keeper mutations confer resistance to MKIs but are overcome by selective RET inhibitors. Solvent front mutations (e.g., RET G10S/C/R) confer resistance to selective RET inhibitors. Mutations or amplifications of MET or NTRK underlie off-target mechanisms of resistance to selective RET inhibitor therapy. EMT may also play a role in acquisition of RET inhibitor resistance.