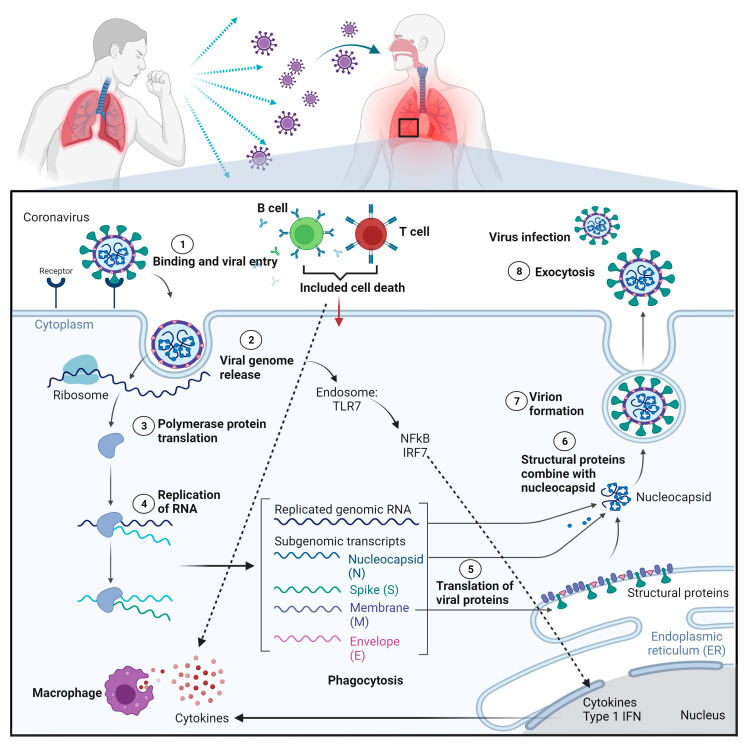
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram representing SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis. The surface S protein facilitates SARS-CoV-2 to enter host cells by attaching to ACE2 in synergy with the host’s TMPRSS2. In the host cells, cascade event of SARS-CoV-2 replication, leading to viral assembly, maturation, and virus release. On the other hand, SARS-CoV-2 RNA will be identified by TLR7 where multiple proteins are recruited to form a complex after viral RNA engages TLR7, which increases the transfer of transcription factors like NF-kB and IRF7 to the nucleus and triggers the release of proinflammatory cytokines that are responsible for the development of sign and symptoms of COVID-19.