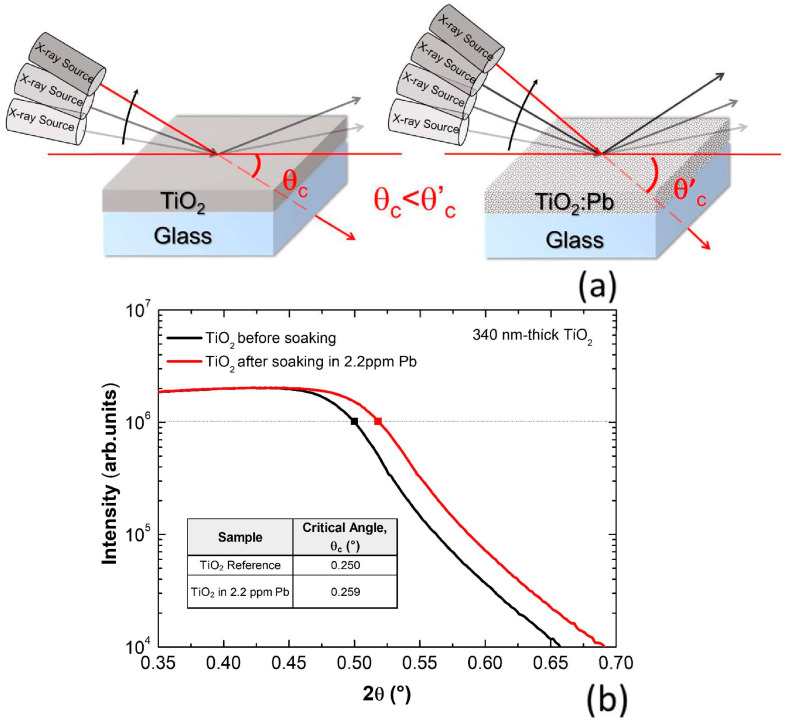
Figure 1.
(a) Schematics of the working principle for X-ray reflectivity analyses on a gig-lox TiO2 sample deposited on a glass substrate. The presence of lead in the gig-lox films causes an increase of the critical angle θc. (b) X-ray reflectivity curves from TiO2 films (340 nm-thick) before and after soaking into an aqueous solution containing 2.2 ppm of Pb. The black line represents the TiO2 sample before soaking and the red line represents the same sample after soaking, with its critical angle shifted rightwards.