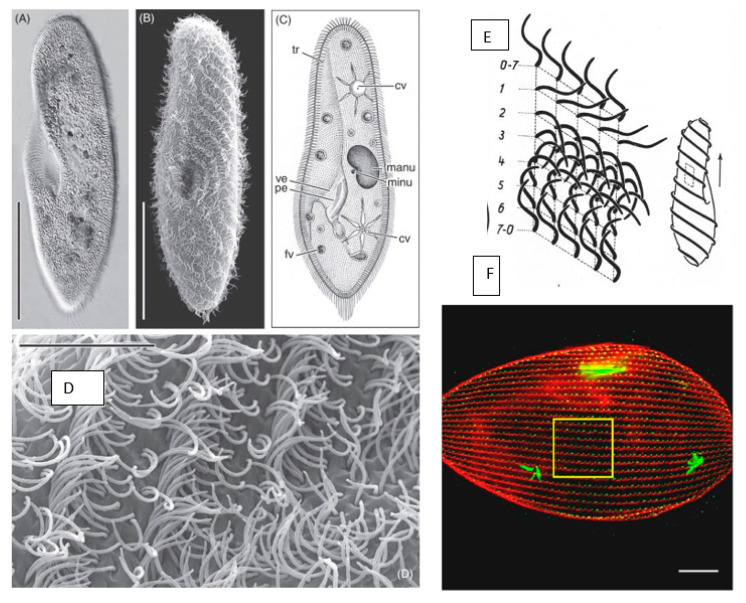
Figure 1.
Panel 1 (A,B): light microscopic appearance of Paramecium caudatum. Panel 1 (C): drawing of Paramecium illustrating light microscopic features: cv contractile vacuoles, fv food vacuoles, manu macronucleus, mino micronucleus, pe peristome, tr trichocysts and ve vestibulum. Panel 1 (D): higher magnification of the metachronal waves of the cilia. Scale bar in (A) and (B) 100 μm; (D) 10 μm. from Figure 1 in [29] and used with permission. Panel (E): form of ciliary stroke and metachrony. Diagrams of instantaneously fixed surface area with five ciliary rows with 0–2 effective, 2–7 recovery stroke. Cell diagram at left shows source of metachronal waves in forward movement. From Grell [32] and used with permission. Panel (F): immunofluorescence image of P. tetraurelia. Basal bodies green (1D5 antibody) and striated rootlets of the basal bodies red (anti-–SR). Straight rows extend between the anterior and posterior poles. [33]; used with permission.