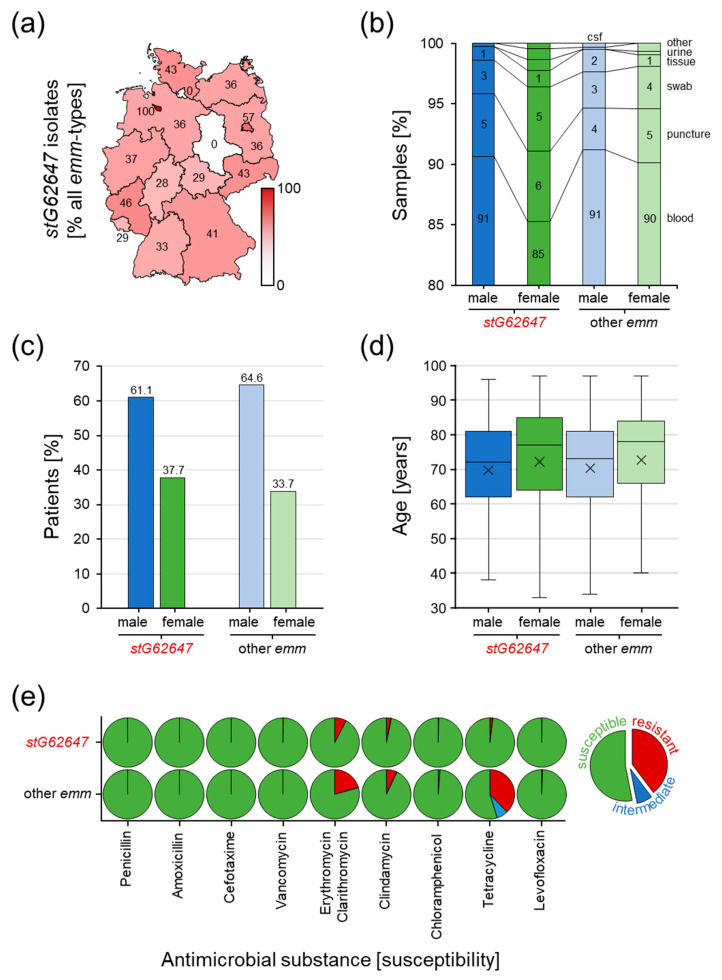
Figure 3.
Analysis of potential differences between invasive SDSE infections associated with stG62647 and other emm types in the national study cohort. (a) Geographical disaggregation of the ratio of stG62647 cases against total invasive SDSE infections (red gradation and values in the map) by the German federal state of the corresponding patient residence. (b) Differences in sample material ratio between stG62647 cases (dark colored columns) and other emm types (light colored columns), discriminating male (blue) and female (green) patients. (c) Comparison of invasive SDSE infections associated with stG62647 (dark colored columns) and all other emm types (light colored columns) of the national study cohort discriminating male (blue) and female (green) patients. (d) Analysis of invasive infections associated with stG62647 (dark colored boxes) and all other emm types (light colored boxes) of the national study cohort regarding age distribution for male (blue) and female (green) patients with the median (line) and arithmetic mean (cross). (e) Susceptibility of stG62647 isolates and isolates of all other emm types of the national study cohort to nine antimicrobial substances, discriminating susceptible (green), intermediate (blue), and resistant (red) following the guidelines of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.