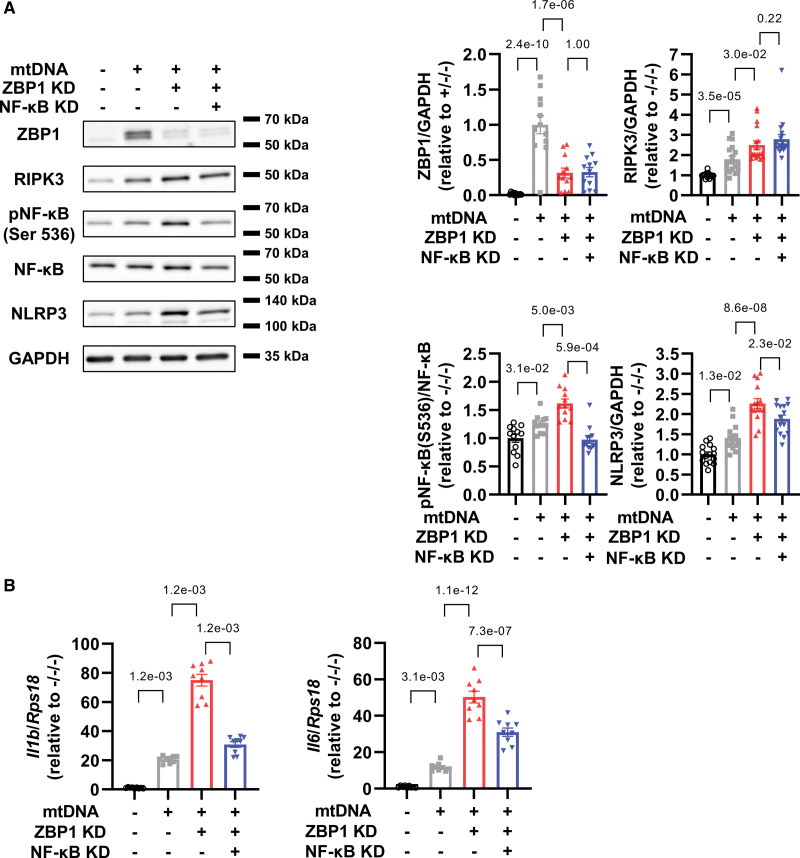
Figure 4.
NF-κB (nuclear factor-κB) knockdown suppresses increases in NLRP3 (nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich-repeat family pyrin domain containing 3) axis by ZBP1 (Z-DNA binding protein 1) knockdown in cardiomyocytes treated with mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). A, Representative immunoblots of ZBP1 (n=12; number of experiments, 4), RIPK3 (receptor interacting protein kinase; n=18; number of experiments, 6), phosphorylated NF-κB (Ser 536), NF-κB (n=12; number of experiments, 4), NLRP3 (n=15; number of experiments, 5), and GAPDH in neonatal rat ventricular myocytes (NRVMs) treated with or without small interfering RNA (siRNA) for ZBP1 (10 nmol/L) and NF-κB p65 subunit (10 nmol/L) in the presence or absence of mtDNA (1000 ng/mL) for 24 hours. B, mRNA levels of Il1b and Il6 in NRVMs treated with or without siRNA for ZBP1 (10 nmol/L) and NF-κB p65 subunit (10 nmol/L) in the presence or absence of mtDNA (1000 ng/mL) for 24 hours (n=9). The experiment was conducted 3×. Error bars denote standard errors. Data were analyzed using the Wilcoxon rank sum test (A, RIPK3 and NF-κB; B, Il1b; adjust=3), and 2-way ANOVA followed by Tukey multiple comparisons test (A, ZBP1 and NLRP3; B, Il6).