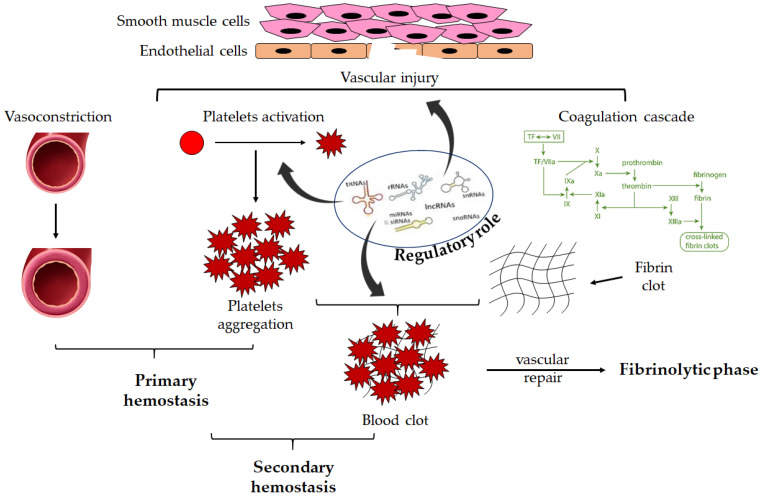
Figure 1.
Overview of hemostasis. Endothelial damage induces activation of the primary hemostasis. Subendothelial thrombogenic material is exposed to the flowing blood. Vasoconstriction and coagulation cascade activation occur. Moreover, the subendothelial matrix proteins bind to receptors on the platelet surface finally resulting in platelet activation and aggregation, leading to platelet plug formation. Secondary hemostasis leads to the formation of fibrin through coagulation proteins and the formation of a blood clot including activated platelets. Once the vessel wall is repaired, the clot is dissolved by fibrinolysis. These processes are regulated via different RNA-related mechanisms.