Table 1.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Product and Difference Methods for Assessing Mediation
| Product Method | Difference Method |
|---|---|
| Advantages | Advantages |
| • Estimator has a causal interpretation if the regression models are correctly specified.• The 2 regression models considered in the product method are always compatible.• Can be extended to accommodate exposure-mediator interaction effect (1, 14).• At least as efficient as the difference method for estimating mediation measures, when the regression models used in product method are correctly specified (primary focus of this article). |
• Only need to model the outcome-exposure relationship with and without adjustment for the mediator, and no need to model the mediator-exposure relationship (2, 7).• Relatively simple and consistent expressions on mediation measures for several main outcome and mediator data types.• Outside the causal inference framework, the regression coefficients in the difference method represent epidemiologic associations (for example, 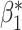 , exposure effect without adjusting for mediator; , exposure effect without adjusting for mediator; 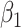 , exposure effect with adjusting for mediator).•
More robust than the product method when the exposure-mediator relationships are misspecified (Web Appendix 4). , exposure effect with adjusting for mediator).•
More robust than the product method when the exposure-mediator relationships are misspecified (Web Appendix 4). |
| Disadvantages | Disadvantages |
| • Need to specify and fit the mediator-exposure relationship, a “nuisance” model that is usually of less interest in epidemiologic studies.• Require distributional assumptions on the mediator when the outcome binary.• Misspecification of the mediator-exposure model (even its error term) may cause severe bias in mediation measure estimation (Web Appendix 4). | • When the binary outcome is common and modeled by logistic regressions, the 2 outcome models under the difference method are not compatible (2) and the difference method can only present conservative NIE estimator (7).• The estimators given by the difference method do not always have causal interpretation (7).• The results are no longer valid in the presence of exposure-mediator interaction effects. |
