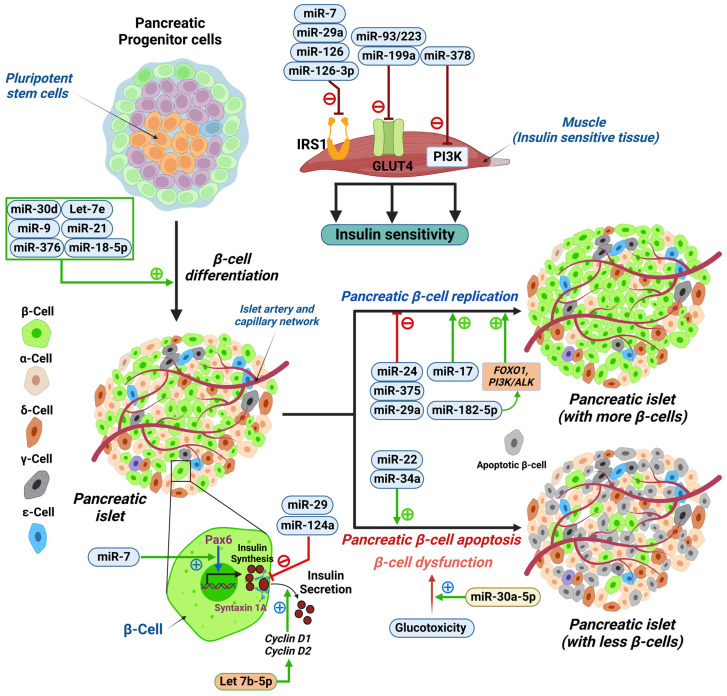
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration showing micro RNAs (miRNAs) involved in pancreatic β-cell differentiation, function, and survival. miRNAs that regulate insulin action in insulin sensitive tissues (muscle, for example) are miR-7, miR-29a, miR-126, and miR-126-3p that negatively regulate IRS1; miR-93/223 and miR-199a that negatively regulate glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4); and miR-378 that negatively regulates phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). miR-30d, let-7e, miR-9, miR-21, miR-376, and miR-182-5p positively regulate pancreatic β-cell differentiation from pancreatic progenitor cells. While miR-24, miR-375, and miR29a negatively regulate pancreatic β-cell replication, miR-17, and miR-182-5p (by activating the FOXO1, PI3K/ALK pathway) is a positive regulator. miR-22 and miR-34a induce pancreatic β-cell apoptosis. miR-30a-5p modulates the glucotoxicity induced β-cell dysfunction. miR-7 positively regulates Paired box protein (Pax-6) to enhance insulin synthesis in β-cells. Let-7b-5p positively regulates insulin secretion by modulating cyclin D1 and cyclin D2. miR-29 and miR-124a negatively regulate syntaxin 1A, which reduces insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells. Pancreatic islets contain insulin producing (β-cells), glucagon producing (α-cells), somatostatin producing (δ-cells), pancreatic polypeptide producing (Ɣ-cells), and ghrelin producing (Ɛ-cells) endocrine cells. FOXO1, Forkhead box protein O1; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase. Illustration created using Biorender.com (with publication license).