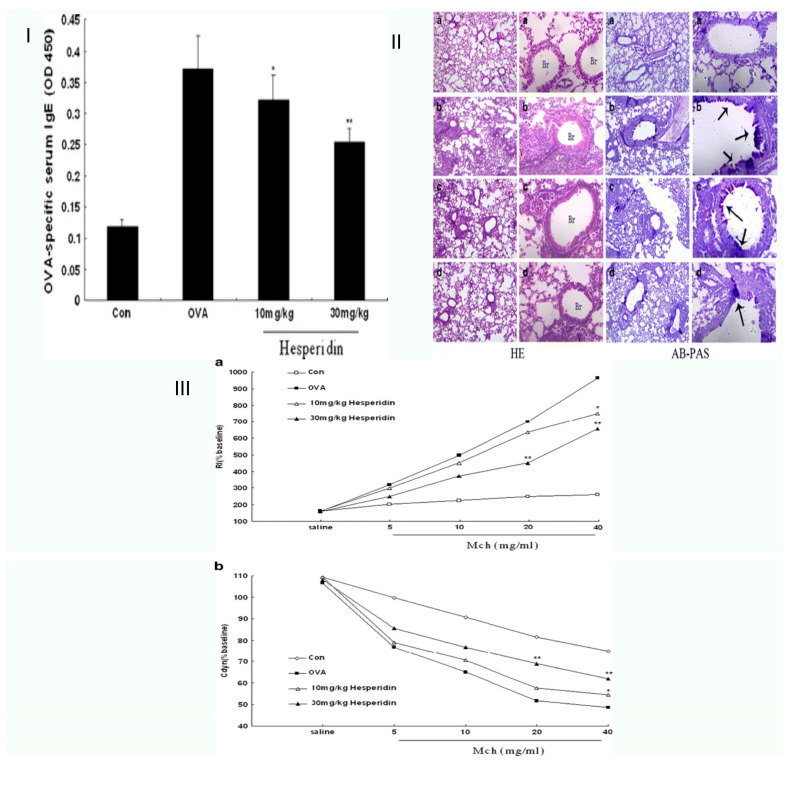
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of hesperidin’s ability to reduce asthma symptoms in an allergic airway inflammation model. (I) Hesperidin’s (milligrams per kilogram) impact on serum OVA-specific IgE. (II) Representative hematoxylin–eosin and alcian blue-periodic acid-Schiff stained sections of lung from: (a) PBS-challenged mice; (b) OVA-challenged mice; (c) OVA-challenged mice treated with hesperidin (10 mg/kg); (d) OVA-challenged mice treated with hesperidin (30 mg/kg). The left panel is magnified 100×; the right panel is magnified 400×. Br bronchi, V vessel. Arrows indicate areas of alcian blue+cells. (III) In response to methacholine, hesperidin therapy decreased RI and restored Cdyn in OVA-challenged mice. Airway hyperresponsiveness was assessed by percentage change from the baseline level of (a) lung resistance (RI, n = 6 mice per treatment group) and (b) dynamic compliance The values represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. vs. OVA [26].