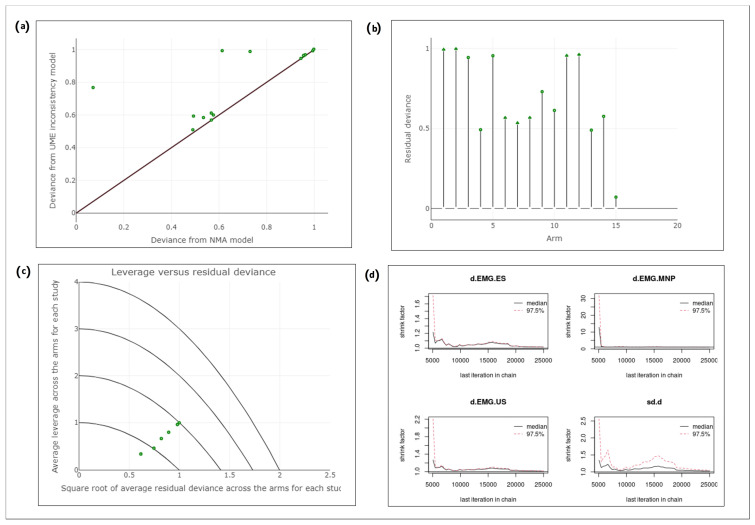
Figure 5.
(a) The NMA/UME residual deviance plot displays the contribution of each data point (study arm) to the residual deviance for the NMA consistency and the UME inconsistency models. If the data points are located on the line of equality, there is no inconsistency, because the model fit does not improve if the UME inconsistency model is applied. Points below the equality line have a better fit for the UME inconsistency model. On the contrary, points above the equality line have a better fit for the NMA consistency model. Hence, data points above or on the equality line have a smaller residual deviance from the NMA consistency model and there is no proof of inconsistency. In our case, all study arms were above or on the equality line, meaning that there was not inconsistency. (b) The stem plot visualizes the posterior residual deviance of each study arm. The shorter the stem, the smaller the residual deviance and thus, the better the model fit. In total, there are 15 study arms and in all cases posterior residual deviance is lower than 1, pointing to a good model fit. (c) The leverage plot is used to evaluate the influence of each data point to the model fit and DIC. The average leverage is depicted on the y-axis and the residual deviance is on the x-axis. There are parabolas characterized by a number, represented by c. Points that lie on each parabola or in-between contribute an amount of c to the model estimation. Points lying outside the curve with c = 3 contribute to a poor model fit. In our study, all study arms lie below the parabola with c = 1.5 and contribute to a good model fitness. (d) Gelman convergence assessment plots for the parameters d.EMG.ES, d.EMG.US and d.EMG.MNP and d.sd. Four Markov chains were used to compute the scale reduction factor. In each case, there were 25,000 iterations and convergence was achieved at 5000 iterations approximately. Variance between and within the chains was almost identical, in other words there was a satisfactory convergence of the Markov chains. The chain steps were stable over the time apart from the d.sd parameter in which they exhibited small divergence. Abbreviations: EMG: electromyography, ES: electrical stimulation, MNP: manual needle placement, NMA: network meta-analysis, sd: standard deviation, UME: unrelated mean effect, US: ultrasound.