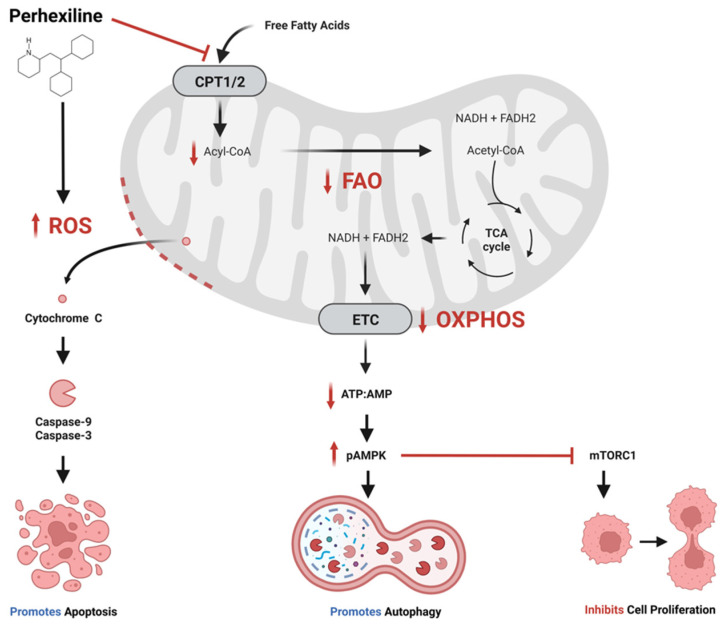
Figure 1.
Proposed anti-cancer effects of perhexiline. Perhexiline inhibition of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) and CPT2 restricts the entry of free fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix, thereby inhibiting fatty acid oxidation (FAO). This may limit the production of the electron transport chain (ETC) co-enzymes nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FADH2), which would inhibit oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) and the generation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). A reduction in ratio of ATP to adenosine monophosphate (AMP) activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) by phosphorylation (pAMPK). pAMPK triggers autophagy, and inhibits cell proliferation by inhibiting mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). Additionally, perhexiline increases the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which compromises mitochondrial membrane integrity, leading to the release cytochrome c and activation caspases that initiate apoptosis. Created with BioRender.com.