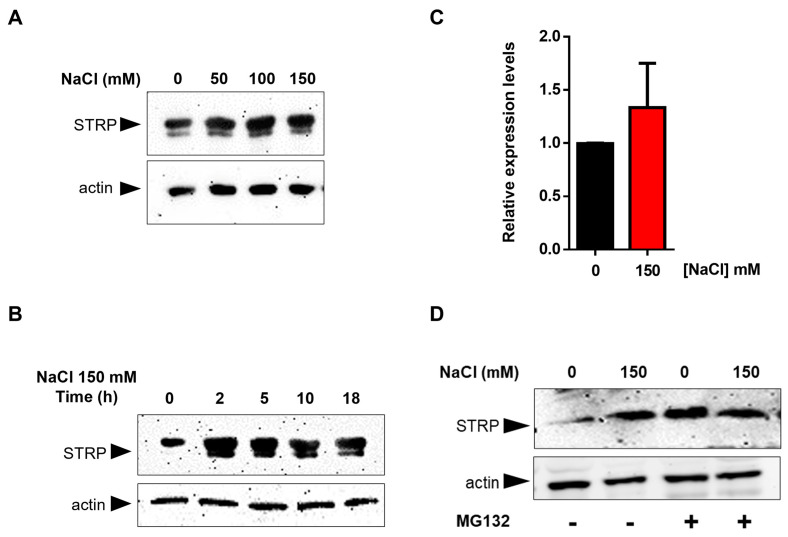
Figure 1.
Salt stress increases STRP levels by inhibiting proteasome–mediated degradation of the protein. Salt Tolerance–Related Protein (STRP) levels were assessed by Western blot on two–week–old seedlings treated with 50, 100, and 150 mM NaCl for 18 h (A) or with 150 mM NaCl for 2, 5, 10, and 18 h (B). Twenty μg of whole cellular extract were separated by SDS–Page, electroblotted on the PVDF membrane, and incubated with the anti-STRP antibodies. Actin was used as a loading control. (C) STRP expression levels under salt stress were determined by RT-qPCR on total RNA extracted from two-week-old A. thaliana seedlings treated with 150 mM NaCl for 18 h. Error bars are s.e.m. of three independent experiments. (D) MG132 treatment was performed on the whole cellular extract of two-week-old seedlings treated with 150 mM NaCl for 18 h. Samples (20 μg) were separated by SDS–Page, transferred on the PVDF membrane, and immunodecorated with anti-STRP and anti-actin antibodies as loading control.