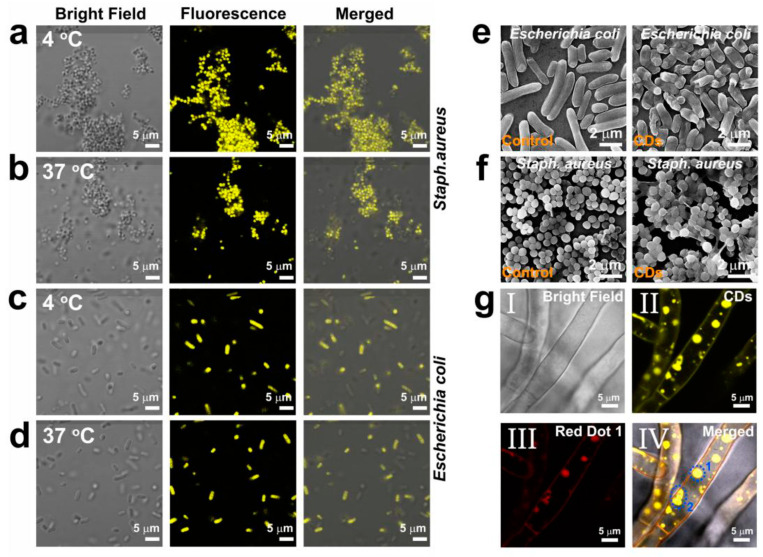
Figure 12.
(a,b) Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) images of S. aureus (Gram-positive) treated with CDs (25 µg mL−1) for 1 h at 4 and 37 °C. (c,d) The CLSM images of E. coli (Gram-negative) treated with CDs (25 µg mL−1) for 1 h at 4 and 37 °C. (λex = 405 nm; emission was collected at 415–550 nm, for both strains). (e,f) SEM images of S. aureus and E. coli after incubation without and with CDs at 60 µg mL−1 for 12 h, respectively. (g) CLSM images of Rhizoctonia solani treated with CDs and Red Dot 1 for 30 min at 37 °C: (I) bright field, (II) CDs (200 µg mL−1; λex = 405 nm; emission was collected at 415−550 nm), (III) Red Dot 1 (200× in water; λex = 543 nm; emission was collected at 580–750 nm), and (IV) merge of images (the blue traces marked 1 and 2 are nucleus and ruptured nucleus, respectively). Reprinted with permission from ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, by Hao Li, Jian Huang, Yuxiang Song, et al., Degradable Carbon Dots with Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Activity, 10, 26936 [262]. Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society.