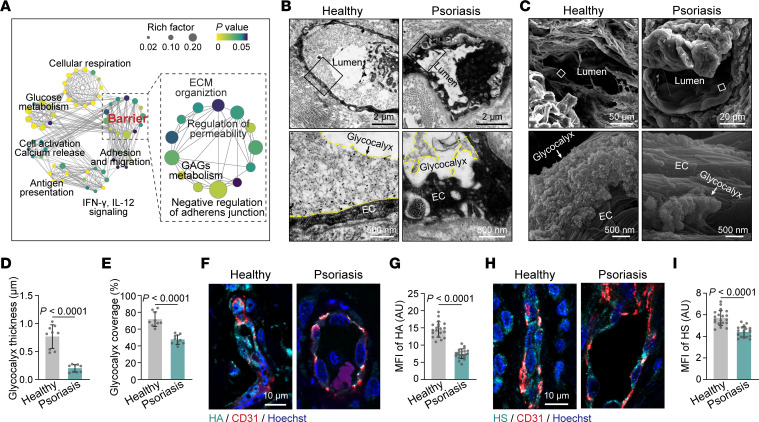
Figure 2. The endothelial glycocalyx is disrupted in psoriatic skin vessels.
(A) Network visualization of pathways enriched in psoriatic capillary ECs compared with healthy capillary ECs. Network nodes, which are colored by adjusted P value and sized by rich factor, represent individual enriched gene sets; edges represent shared genes between nodes. (B and C) TEM and SEM showing the endothelial glycocalyx in skin blood vessels from healthy individuals and psoriasis patients (n = 3 skin samples/group). The endothelial glycocalyx is highlighted by the yellow dotted line. (D and E) Average endothelial glycocalyx thickness and coverage in skin vessels of healthy individuals and psoriasis patients (n = 9 vessels of 3 skin samples/group). (F and G) Immunofluorescence and MFI quantification of HA on skin ECs from healthy subjects and psoriasis patients (n = 21 vessels of 7 skin samples/group). (H and I) Immunofluorescence and MFI quantification of HS on skin ECs from healthy subjects and psoriasis patients (n = 21 vessels of 7 skin samples/group). Data are represented as mean ± SD. Analysis was performed using unpaired Student’s t test.