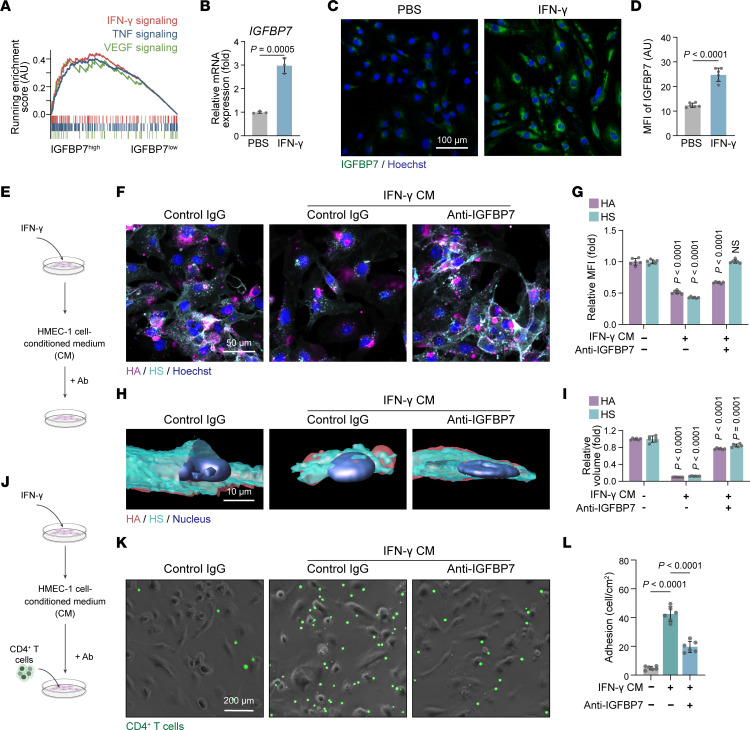
Figure 8. Anti-IGFBP7 treatment rescues IFN-γ–induced endothelial glycocalyx destruction and T cell adhesion.
(A) GSEA revealing the signaling pathways enriched in IGFBP7hi psoriatic ECs compared with IGFBP7lo psoriatic ECs. (B) Relative mRNA expression assessed by quantitative real-time PCR of IGFBP7 in HMEC-1 cells (n = 3/group) treated with PBS or IFN-γ. (C and D) Representative staining and MFI quantification of IGFBP7 in HMEC-1 cells (n = 6/group) treated with PBS or IFN-γ. (E) HMEC-1 cells stimulated with different conditioned media (CM) were treated with anti-IGFBP7 or control IgG. (F and G) Representative staining and MFI quantification of HA and HS (n = 6/group). (H and I) 3D reconstruction and volume quantification of HA and HS (n = 6/group). (J) HMEC-1 cells stimulated with different conditioned media were first treated with anti-IGFBP7 or control IgG and then cocultured with CD4+ T cells. (K and L) Representative images and quantification of adherent CD4+ T cells in the coculture assay (n = 6/group). Data are represented as mean ± SD. Data in B and D were analyzed using unpaired Student’s t test. Data in G, I, and L were analyzed using 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. Labeled P values in G and I represent the differences between the corresponding group and the control group.